
 What is a Geomagnetic Disturbance?
What is a Geomagnetic Disturbance?
A geomagnetic disturbance occurs when the Earth’s magnetosphere is disrupted due to interactions with solar wind, leading to changes in magnetic field strength and plasma flow.
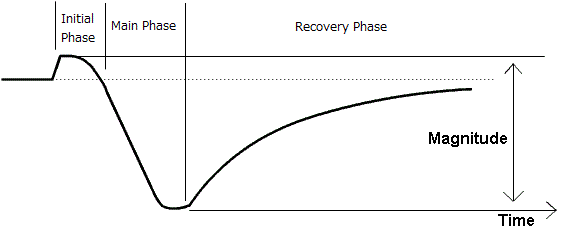
Figure 1: Geomagnetic Disturbance based on Kakioka Magnetic Observatory, Japan ↗
This is a typical morphology of sudden-commencement type magnetic storms (horizontal force variation).
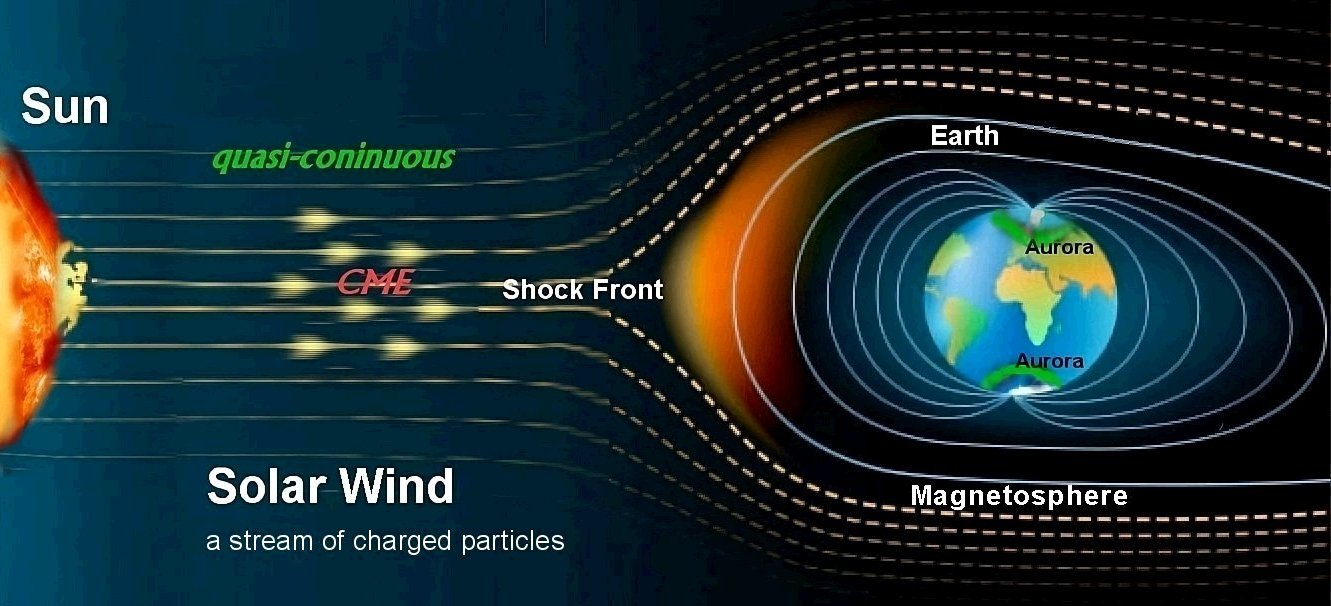
Figure 2: The solar wind interacts with Earth’s magnetosphere causing auroras.
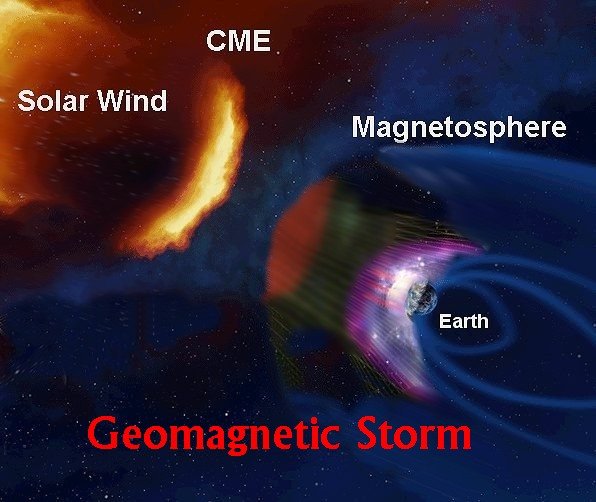
Figure 3: Interaction between a CME and Earth's Magnetosphere
A major magnetic storm may block HF propagation (3–30 MHz) by modifying the distribution of free-electrons in the ionosphere.
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.