
 What are Solar Flares?
What are Solar Flares?
Solar flares are explosive bursts of soft X-ray radiation (0.1–1 nm), triggered by intense magnetic fields around sunspots.
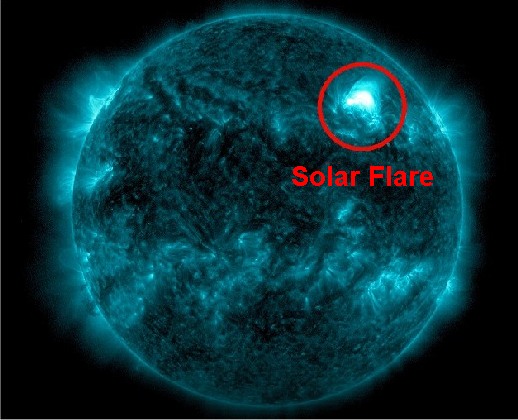

A solar flare courtesy of NOAA, May 2023
When this energetic radiation reaches Earth it enhances the D-region of the ionosphere, causing "fadeout" and/or "radio blackout" events. Flares can last from tens of seconds to several hours.
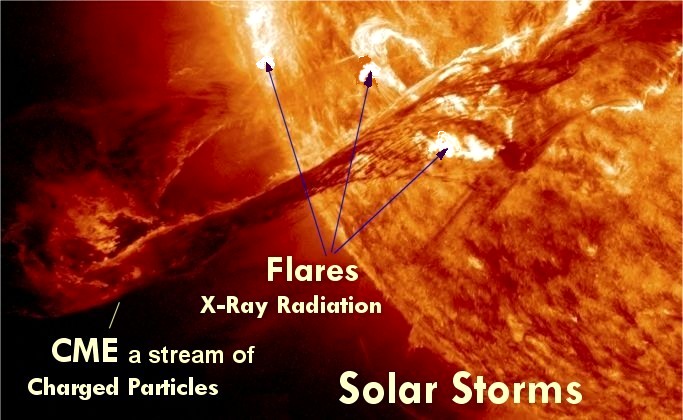
Image credit: NASA, Aug. 2012; captions added by 4x4xm.
Solar X-ray flares usually occur in active regions on the Sun, marked by strong magnetic fields associated with sunspot groups. The intensity of solar flares is classified based on peak emission in the 0.1 - 0.8 nanometes.
NOAA categorizes flares into different levels: A, B, C, M, and X. Radio blackouts are classified using a six-level NOAA Space Weather Scale, R0-R5. The correlation between the solar flare classification and radio blackout scale:
| Solar Flare Class ↗ | A | B | C | M | X | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Blackout Scale ↗ | R0 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | ||
The recent 3 days of solar flares | The current solar flare 
- References:
- Solar Flares (Radio Blackouts) NOAA / NWS Space Weather Prediction Center
- Types of Space Weather Storms
- Communications blackout Wikipedia
- Radio Blackout UNDRR
- Solar flare alert radio hams Find on this site
- Solar flare alert warning Find on this site
- Solar flares hitting earth today Find on this site
- Solar flares today alerts warnings Find on this site
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.