What is Solar Wind?
What is Solar Wind?
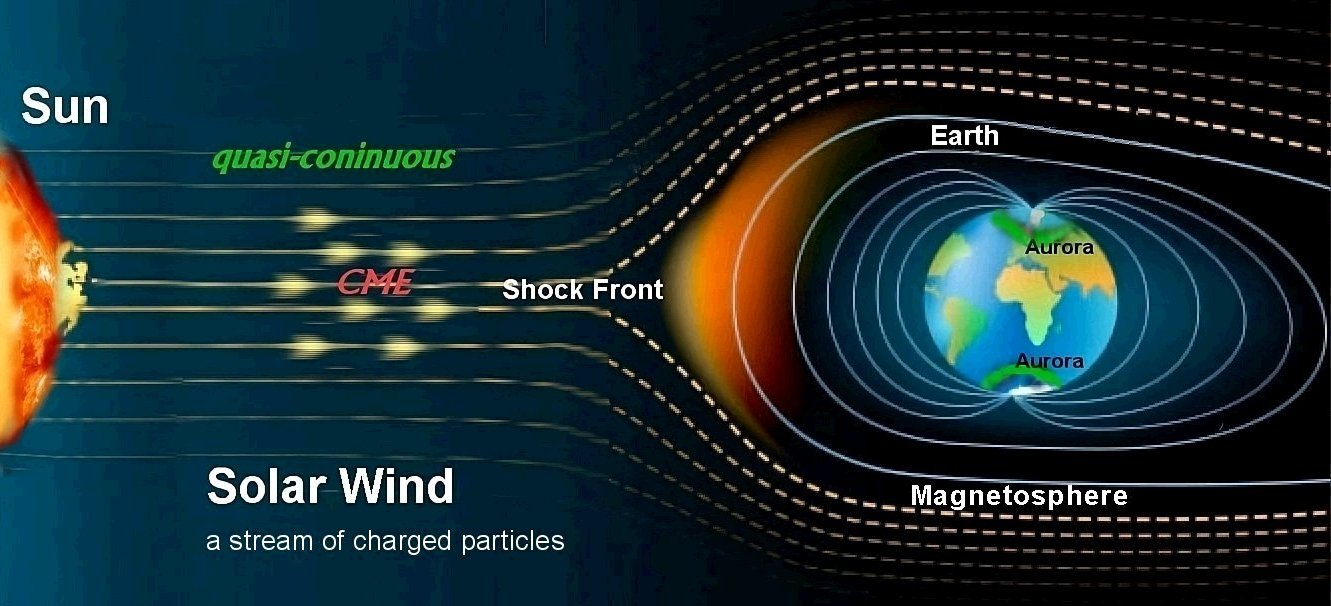
The solar wind is a fast-moving stream of charged particles (plasma) that emerges from the sun. It travels around the solar system, carrying with it the magnetic field of the sun.
An illustration showing how the solar wind rearranges Earth's magnetosphere, compresses the magnetic field on the side facing the sun while elongating it on the opposite end.The solar wind is a major factor affecting the space environment around the Earth and other planets. On Earth it causes phenomena such as auroras, geomagnetic storms, and radiation belts.
- The solar wind's plasma consists mostly of electrons (~47%), protons (~47%), and alpha particles (~5%). It also includes tiny amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, iron, phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes.
- Different parts of the Sun produce solar wind at different speeds. Coronal holes, found near the Sun's poles, create fast solar wind, moving at 500 to 800 kilometers per second. The equator produces slower solar wind, moving at about 400 kilometers per second.
- Far from the Sun, the solar wind reaches speeds of 250–750 km/s and is "supersonic," meaning it moves faster than fast "magnetosonic waves." It slows down at the termination shock near Earth. The solar wind causes phenomena like the aurora (northern and southern lights), comet tails that always point away from the Sun, and geomagnetic storms that can change magnetic field lines.
- The solar wind varies in density, temperature, and speed over time and across solar latitudes and longitudes. Its particles escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy from the corona's high temperature, resulting from the coronal magnetic field.
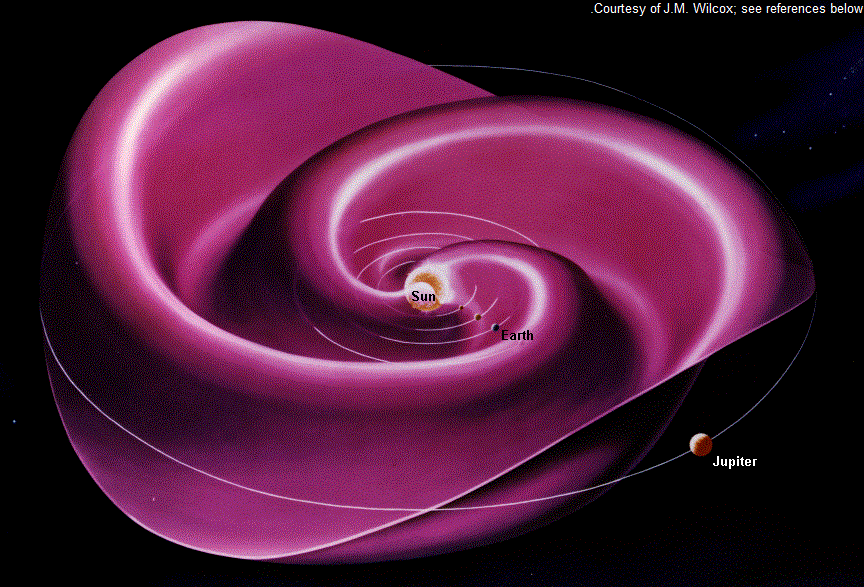
- When solar activity is low, the solar wind and its current sheet (a thin, wide sheet of slow wind) are flat. When solar activity increases, the wind forms a spiral with varying speeds and densities, like a "twirling ballerina's skirt".
- Fast wind catches up to slower wind, creating areas with dense and strong magnetic fields called corotating interaction regions.
- The Sun rotates every 27 days, affecting the solar wind. As the Sun turns, different regions send out varying wind speeds, creating a complex pattern.
- Earth's position in this "ballerina skirt" of solar wind affects space weather.
- Fast winds cause geomagnetic storms, while slow winds bring calm conditions. Monitoring and forecasting the solar wind helps predict space weather impacts on Earth.
- The solar wind causes phenomena like the aurora (northern and southern lights), comet tails that always point away from the Sun, and geomagnetic storms that can change magnetic field lines.
What are Solar Proton Events?
Solar Proton Events are defined as a flux (of protons with energies higher than 10MeV) greater than 10 particles cm-2 s-1 ster-1 (per centimeter-squared per second per steradian) for more than fifteen minutes. The protons travel along the extended magnetic field lines of the Sun, some making their way to the Earth.
Proton Flux Scale (NOAA S-Scale classification)
S-scale thresholds (10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 pfu), based upon values observed or expected on the primary GOES satellite. The ≥100 MeV products are based on a single flux threshold of 1 proton flux unit (pfu) = 1 proton/(cm² s sr).
Proton Events Forecasts
Proton forecasts indicate the percent chance that a proton event may occur during the following three days. Proton events are associated with impacts on HF radio communication, satellite operations and can be biologically hazardous to astronauts or aircrew at high latitudes.
Proton forecasts are daily probabilistic forecasts, ranging from 1% (0.01) to 99% (0.99), of the likelihood of greater than 10 MeV Proton Event occurring within the specified 24-hour day. Proton forecasts are part of the 3-day Forecast and Forecast Discussion products sent twice daily at 00 UTC and 12 UTC by the Space Weather Prediction Center.
The event threshold for Proton Flux is 10 pfu (particle flux unit = particles / cm2-s-sr) at greater than 10 MeV as measured by the NOAA GOES spacecraft.
The NOAA Space Weather Scale for Radiation Storms describes the effects that can be experienced as the result of elevated levels of radiation that occur when the numbers of energetic particles increase.
Proton Alerts
Proton alerts indicate that a proton event is currently in progress. Proton events are associated with impacts on HF radio communication, satellite operations and can be biologically hazardous to astronauts or aircrew at high latitudes. Proton Alerts are disseminated when the Proton Flux is 10, 102, 103, 104 and 10 5 pfu (particle flux unit = particles / cm2-s-sr) at greater than 10 MeV as measured by the NOAA GOES spacecraft.
A separate alert is issued when the Proton Flux is 1 pfu at greater than 100 MeV as measured by the NOAA GOES spacecraft.
Proton Summaries are sent at the end of a significant flare event to notify customers of the maximum Proton Flux reached during the event.
The NOAA Space Weather Scale for Radiation Storms describes the effects that can be experienced as the result of elevated levels of radiation that occur when the numbers of energetic particles increase.
| Aspect | Electrons | Protons |
|---|---|---|
| Aurora Creation | Collide with atmospheric gases, creating visible auroras. | |
| Effect on Ionosphere | Enhance the D-region, causing polar cap absorption (PCA) of HF radio waves. | More of the same, especially during radiation storms. |
| HF Wave Propagation | Lower HF band absorption increases due to higher D-region absorption in polar zones; interruptions occur mostly during auroral activity. | More of the same but disruptions especially during radiation storms and in polar regions. |
Discover how the solar wind affets skywave propagation.
See also an index of terms for HF Radio propagation.
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.