
 What causes geomagnetic storms?
What causes geomagnetic storms?
Solar storms induce geomagnetic storms.
Geomagnetic storms occur when solar activity disturbs Earth’s magnetosphere. Key causes include:
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): Massive bursts of solar plasma and magnetic field released into space.
- High-Speed solar wind streams (HSS): Faster-than-normal streams of solar wind from coronal holes.
- Solar flares: Sudden flashes of brightness often associated with CMEs.
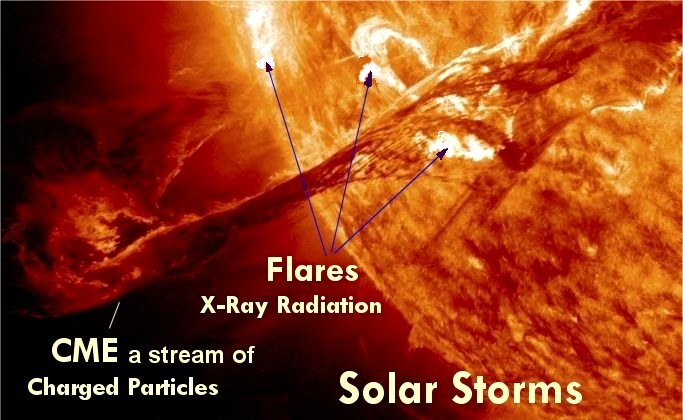
Fig 1. The components of solar storms are solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CME)
Image credit: NASA, Aug. 2012; captions added by 4x4xm.
The sun's magnetic field undergoes a periodic reversal, flipping its polarity in an approximately 11-year cycle. This process is associated with various solar phenomena, such as sunspots, flares, and coronal mass ejections (CME) ↗.
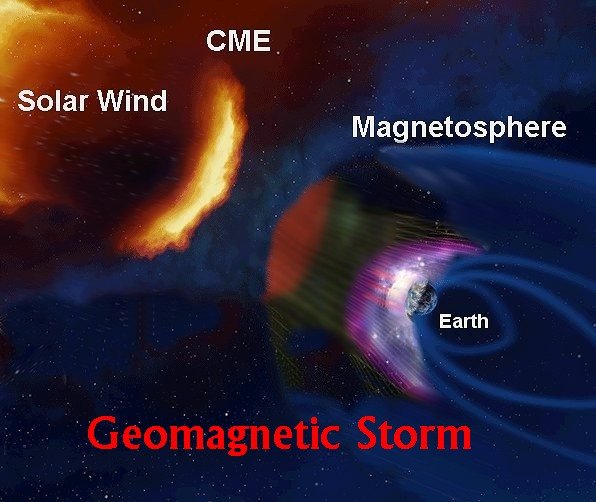
Figure 2: Interaction Between Earth's Magnetosphere and Solar Activity
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.