 What are Geomagnetic Storms?
What are Geomagnetic Storms?
Geomagnetic Storms are disturbances in the Earth's magnetic field, that can last from hours to days.
Geomagnetic Storm Dynamics
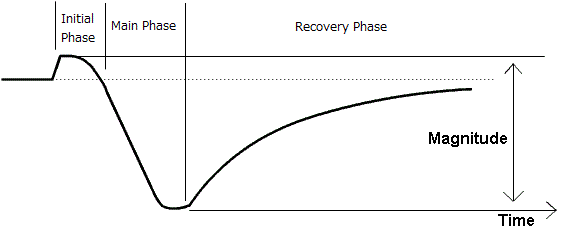
Figure 1: Geomagnetic Storm Dynamics based on Kakioka Magnetic Observatory, Japan ↗
This is a typical morphology of sudden-commencement type magnetic storms (horizontal force variation).
A geomagnetic storm has three phases: initial, main, and recovery. The initial phase involves an increase in the Disturbance Storm Time (Dst) index ↗ by 20 to 50 nano-Tesla (nT) in tens of minutes. The Dst index estimates the globally averaged change of the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field ↗ at the magnetic equator based on measurements from terrestrial magnetometer stations ↗. Dst is computed once per hour and reported in near-real-time.
What are the impacts of a major geomagnetic storm?
A major geomagnetic storm can disrupt HF propagation by changing the distribution of free electrons in the ionosphere. It may also trigger auroras ↗.
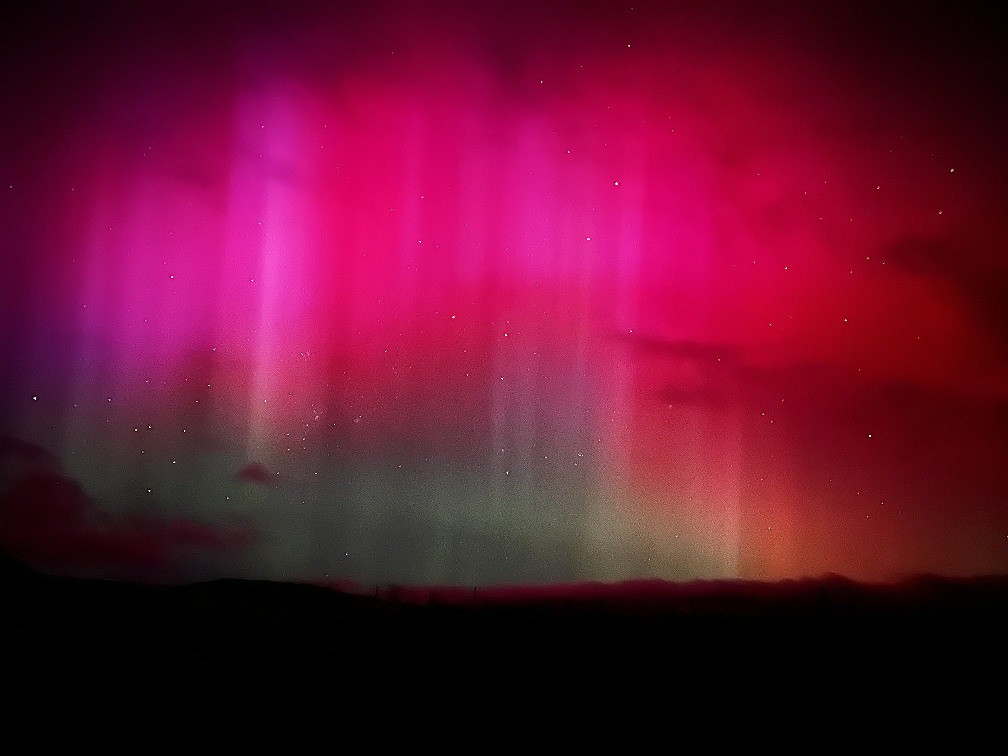




Figure 2: Illustrations of geomagnetic storms as seen from earth close to polar regions (public domain images)
What causes a geomagnetic storm? — Solar radiation bursts and solar energetic particles:
- Solar X-Ray radiation bursts known as solar flares:
- Solar plasma particles colliding with Earth's Magnetosphere.
Significant events are named "Coronal Mass Ejections" (CME) :
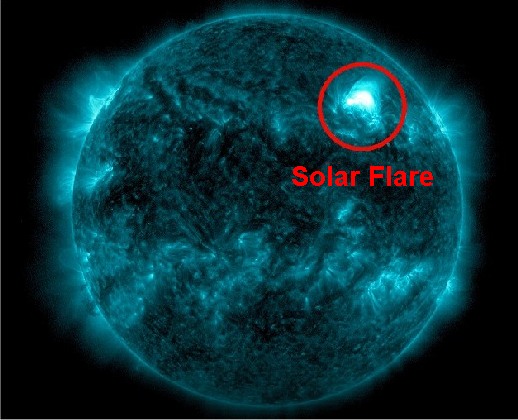

Figure 3: A Solar Flare courtesy of NOAA, May 2023
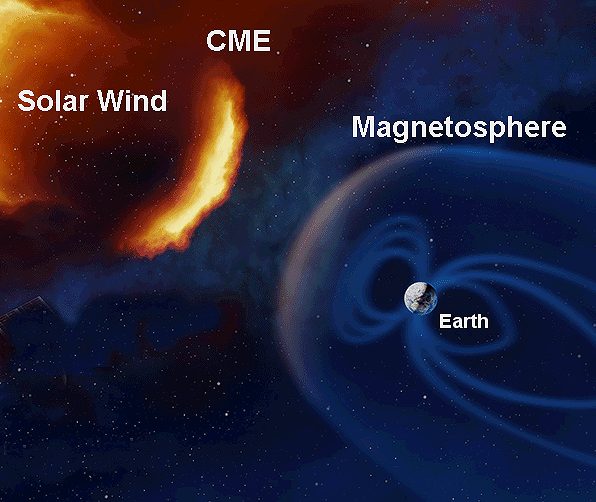
Figure 4: Magnetosphere shields Earth from CME
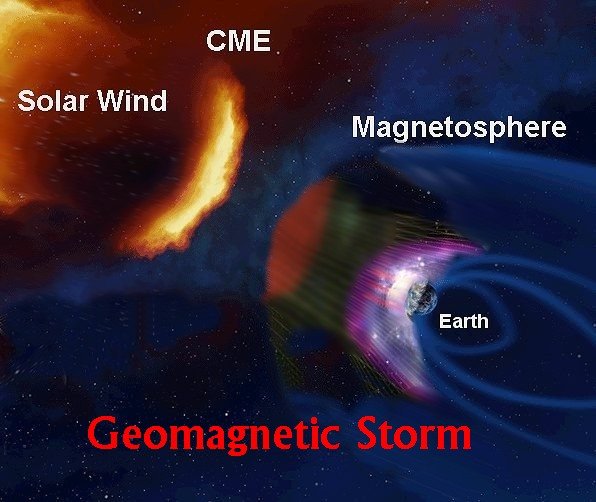
Figure 5: Artist view of a Geomagnetic Storm
How are geomagnetic storms defined?
A geomagnetic storms are defined by changes in the "Disturbance-storm time" (Dst) index. The Dst index estimates the globally averaged change of the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the magnetic equator based on measurements from a few magnetometer stations. Dst is computed once per hour and reported in near-real-time.
How are geomagnetic storms classified?
At quiet time (no storm) ranges from +20 to −20 nano-Tesla (nT). The magnitudes of storms are classified as moderate (from 50 nT to 100 nT), intense (from 100 nT to 250 nT), or super-storm (above 250 nT).
How are geomagnetic storms quantified?
The Kp index quantifies the geomagnetic disturbances, "correlating with G-scale".
What was the strongest geomagnetic storm in history?
The Carrington Event was the most profound geomagnetic storm ever recorded, peaking on September 1–2, 1859, during solar cycle 10. There were several global accounts of its powerful auroral displays, as well as the sparks and fires it generated in telegraph stations. Wireless radio transmissions were unknown at that time.
When was the last significant geomagnetic storm?
The strongest geomagnetic storm in over two decades dazzled scientists and sky-watchers alike in May 2024, during solar cycle 25.

Figure 6: NOAA issued an alert on May 10, 2024, regarding the anticipated G5 storm.
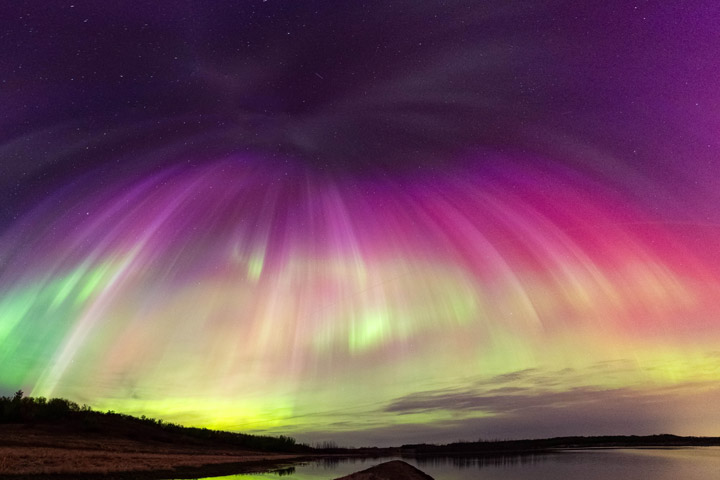
The G5 storm culminated in a remarkable display of the aurora overnight on May 10–11, visible from many areas worldwide, including latitudes where sightings of auroras are uncommon. Photographers and aurora chasers captured the striking range of colors in ground-based photos, some of which they shared with NASA’s Aurorasaurus project.
This photo shows the sky on May 11, looking south from near Saskatoon in Saskatchewan, Canada.
The geomagnetic indices that characterized that May 11, 2024, storm
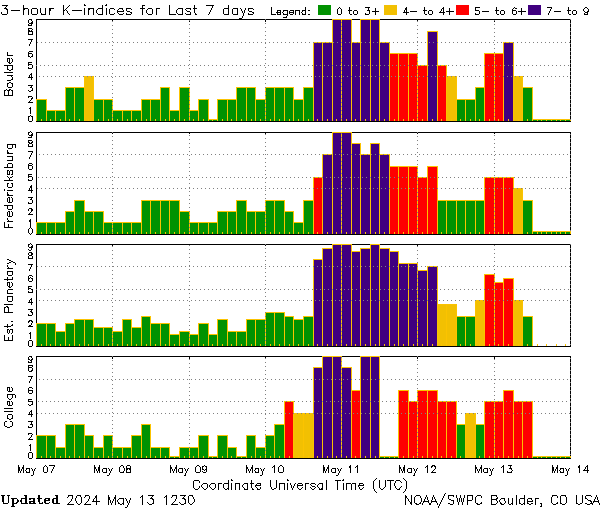
Figure 8: The K index at three stations and the estimated Kp, 2024 May 7–13
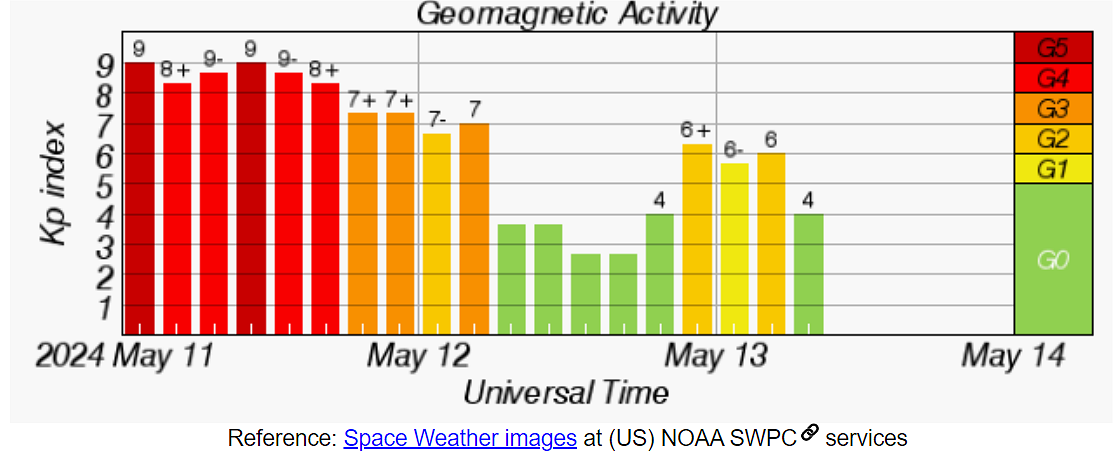
Figure 9: The "Planetary"—Kp Index, 2024 May 11-13
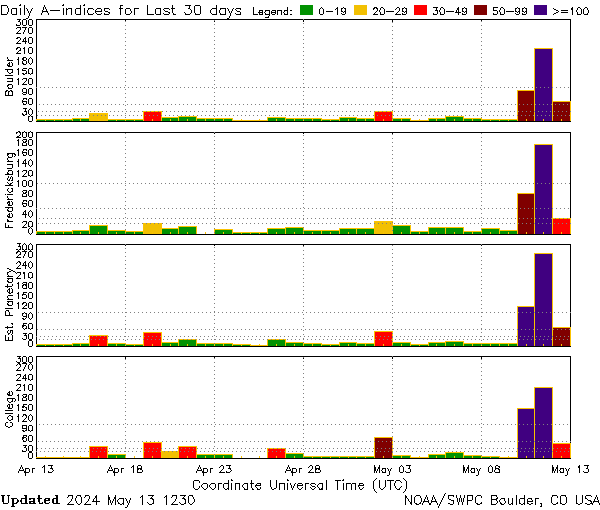
Figure 10: The A-index, 2024 May 7-13
The observed geomagnetic storms from May 11 to May 13, 2024 courtesy of NOAA
- References:
- May 2024 Solar Storms Wikipedia
- Historic Geomagnetic Storm Dazzles NOAA
- Geomagnetic Storms May 2024 Duckduckgo
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.
