What causes ionospheric ionization?
What causes ionospheric ionization?
Understanding Ionization
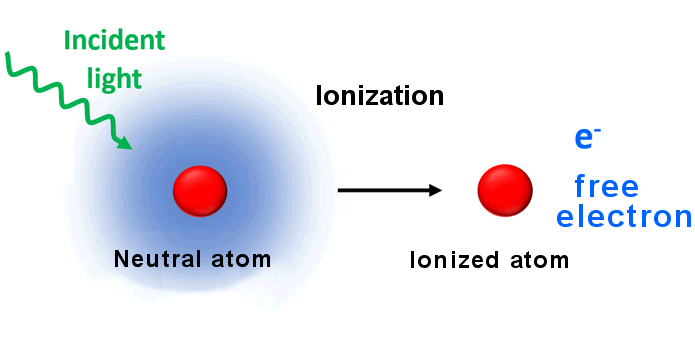
An ion is an atom or molecule with an unbalanced electric charge. Ionization occurs when ultraviolet (UV) light knocks electrons off atoms or molecules, leading to plasma.
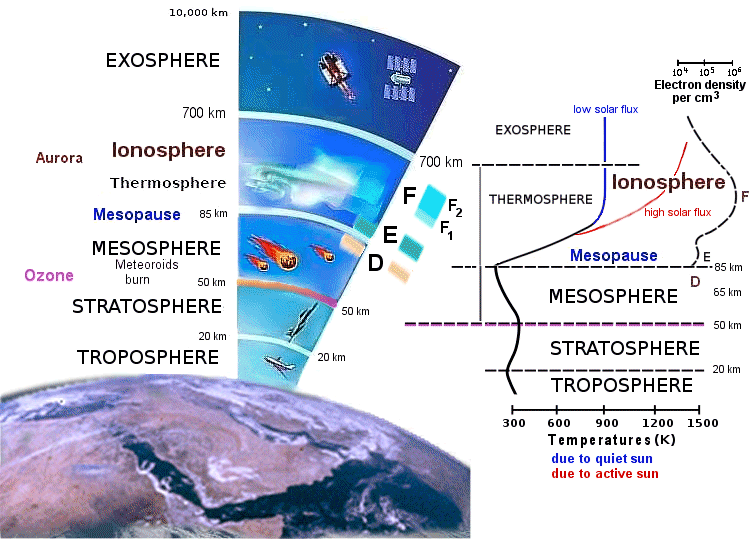
What is Earth's Ionosphere?
Factors Affecting Ionospheric Structure
- Solar Activity: Sunspots, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and variations in solar flux.
- Seasonal Changes: The ionosphere's density and behavior vary across different seasons.
- Time of Day: Differential heating of the atmosphere and Earth's rotation cause fluctuations.
- Atmospheric Tides: The movement of atmospheric waves affects ionization patterns.
- Electromagnetic Influences: Differential charges, such as those from lightning, play a role.
How does the sun affect ionization?
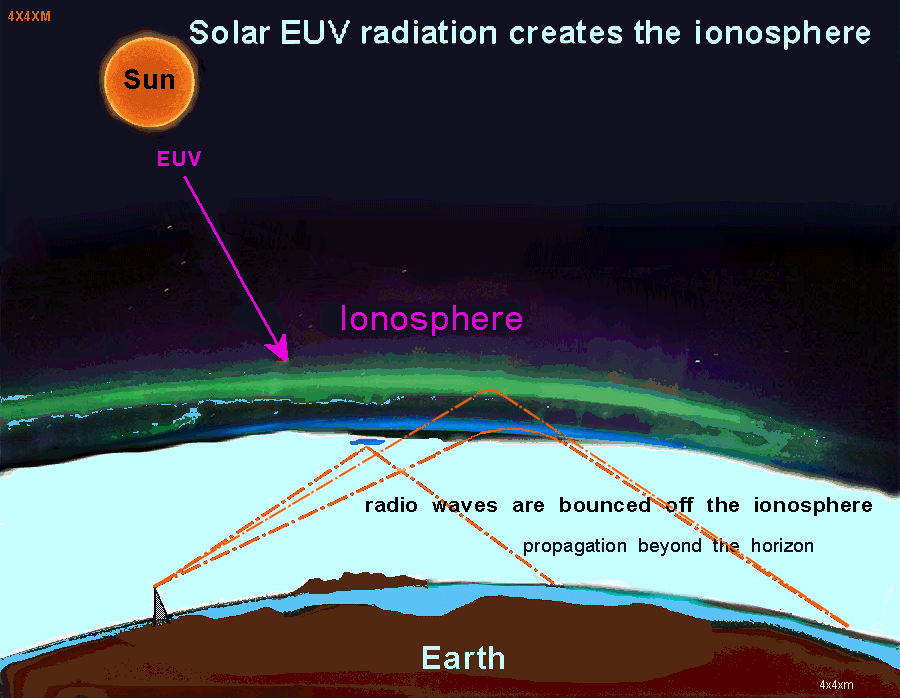
Figure 3 illustrates how the solar EUV radiation ionizes atoms in the upper atmosphere, creating the ionosphere—a dynamic plasma region that enables HF skywave communication.
References & Further Reading
- NASA - Space Weather & Ionosphere
- NOAA - Ionospheric Studies
- ScienceDirect - Research on Ionospheric Physics
- Skywave Propagation
The project "Understanding HF Propagation," focuses on skywave propagation,
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.