
 What Are Radio Waves?
What Are Radio Waves?
- What is a wave?
A wave is a periodic disturbance that transfers energy through space and time. Waves manifest in various forms depending on the medium and type of energy involved.
- 🌊 Water waves are disturbances in the surface level of water.
- 🔊 Sound waves are fluctuations in air pressure or density.
- 📡 Radio waves are oscillations in electric and magnetic fields.Some waves—like water and sound—require a physical medium to travel through, known as mechanical waves. Others, such as radio waves, can propagate through the vacuum of space, and are classified as electromagnetic waves.
- What is radio?
Radio is a form of electromagnetic energy with low-frequency, long-wavelength waves.
- Essence and basic nature of radio waves🗗
Oscillating electric and magnetic fields produce electromagnetic (EM) radiation.
Radio waves are part of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum that travel at the speed of light.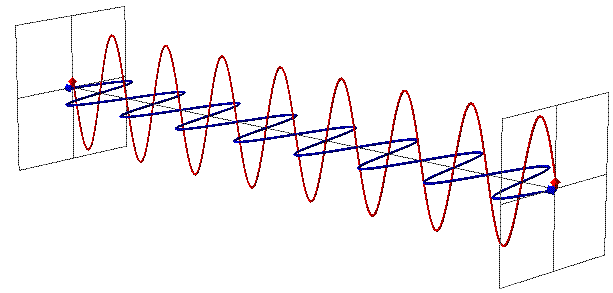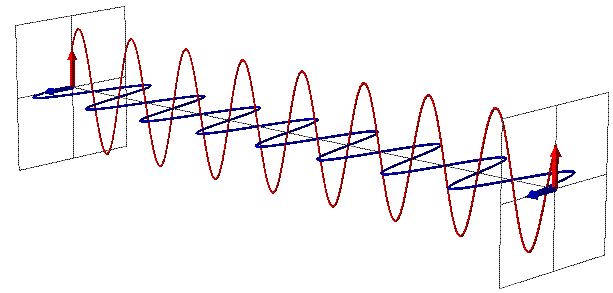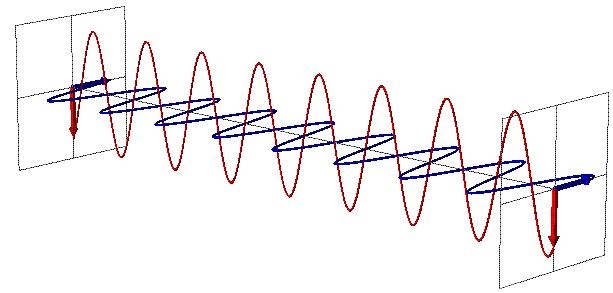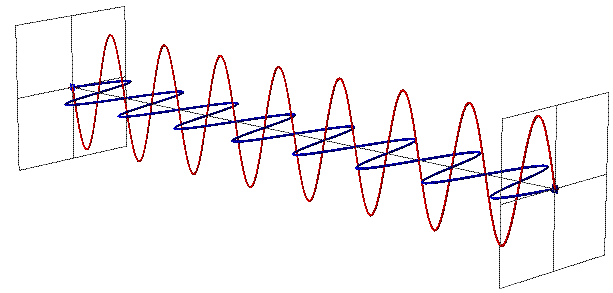
Figure 1: A dynamic illustration of electromagnetic wave - Wavelength, frequencies🗗
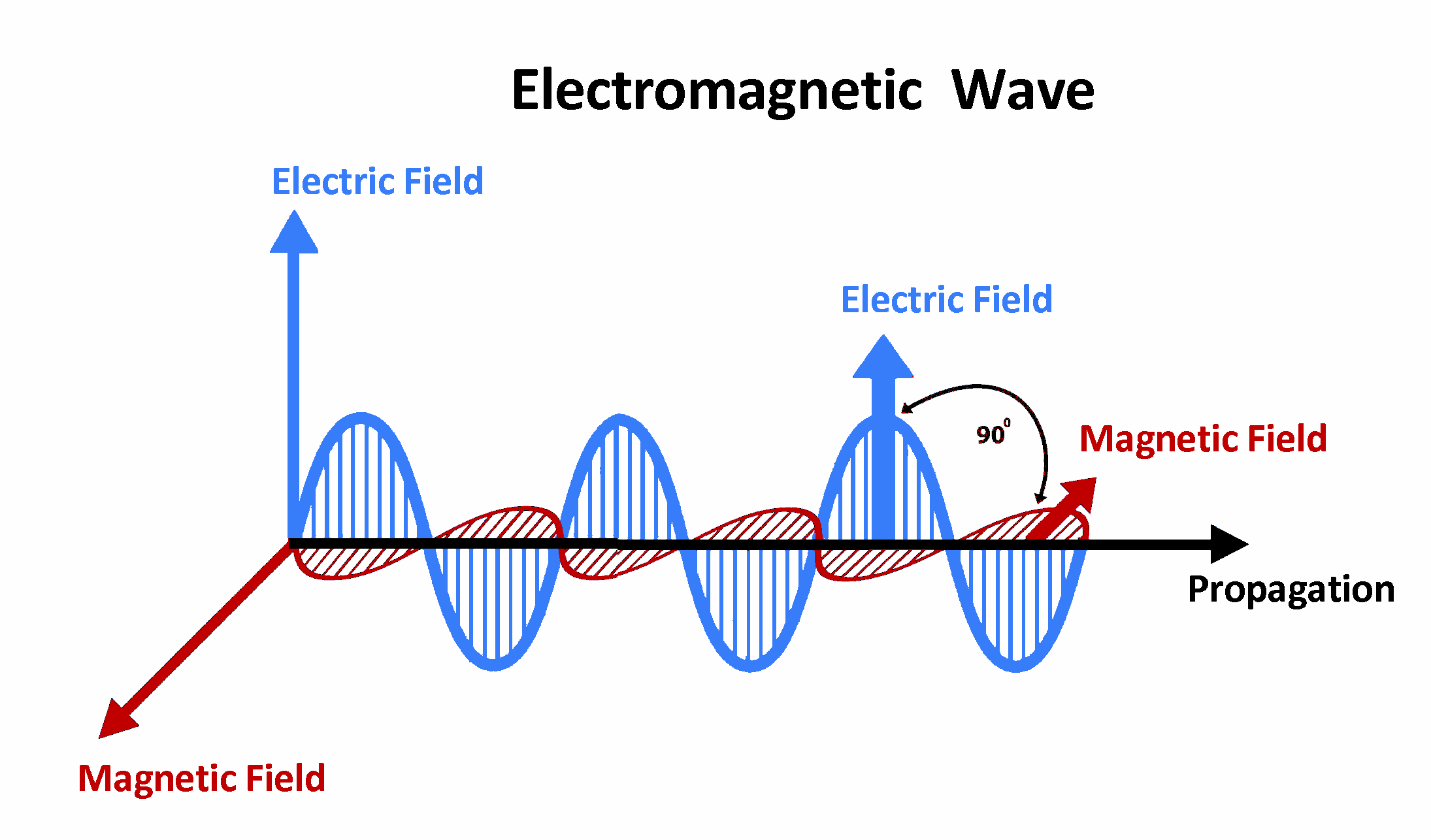
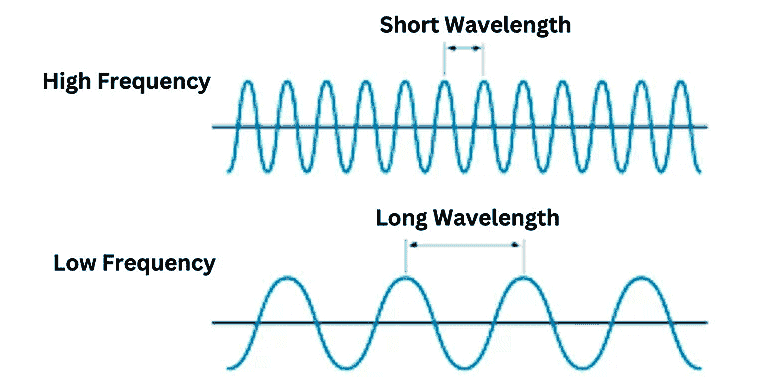
Figure 2: Electromagnetic wave fields and propagation Figure 3: A wave characterized by frequency and wavelength Radio waves have two important properties: frequency and wavelength.
- Frequency (f): Cycles per second (Hertz).
- Wavelength (λ): Distance between successive wave crests. Formula:
c = f*λ, where c is light speed.
- The electromagnetic spectrum:
Radio waves are a subset of the electromagnetic spectrum that has unique applications based on frequency and wavelength.
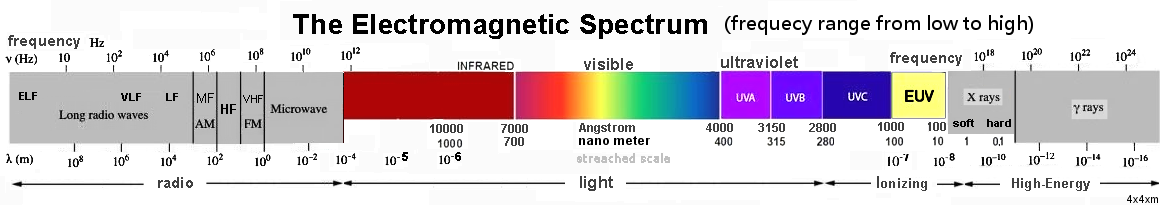
Figure 4: The electromagnetic spectrum - The radio spectrum shown below goes from low to high frequency (long to short wavelength).
Radio wavelengths range from less than a millimeter to over 100,000 kilometers (10-3 - 108 meter); frequencies 3 Hz - 300 GHz.
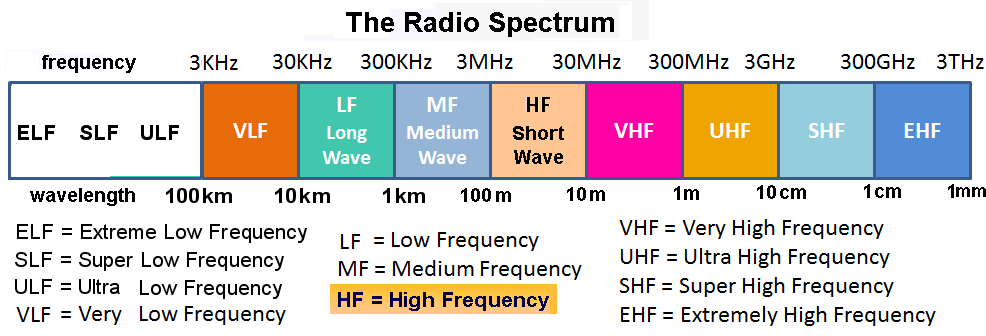
Figure 5: The radio spectrum is divided into 12 bands, each spanning an order of magnitude, ranging from 3 Hz to 3 THz.
Table 1: Eleven bands of radio waves based on frequency and wavelength (THF excluded)Band name abbr. ITU
bandFrequency Wavelength ** Bands
Allocated to
AmateursExtremely low frequency ELF 1 3 - 30 Hz 10,000-100,000 km none Super low frequency SLF 2 30 - 300 Hz 1,000 - 10,000 km none Ultra low frequency ULF 3 300 Hz - 3 kHz 100 - 1000 km none Very low frequency VLF 4 3 - 30 kHz 10 - 100 km none Low frequency
Longwave (LW)*LF 5 30 - 300 kHz 1 - 10 km 2200 m Medium frequency
Medium-wave (MW)*MF 6 300 - 3000 kHz 100 - 1000 m 630, 160 m High frequency
* Short-wave (SW)HF 7 3 - 30 MHz 10 - 100 m 80, 60, 40,
30, 20, 17,
15, 12, 10 mVery high frequency VHF 8 30 - 300 MHz 1 - 10 m 6, 4, 2, 1.25 m Ultra high frequency UHF 9 300 - 3000 MHz 10 - 100 cm 70, 23, 13 cm Super high frequency SHF 10 3 - 30 GHz 1 - 10 cm 5, 3, 1.2 cm Extremely high frequency EHF 11 30 - 300 GHz 1 - 10 mm 6, 4, 1 mm * Short-wave (SW): Historical term used in the first half of the 20th century.
** Amateur radio frequency allocations vary worldwide. While amateurs globally utilize various bands, the majority fall within the high-frequency range. Some bands, however, are restricted to national or regional use due to competing allocations, particularly in the LF, MF, VHF, and UHF segments of the radio spectrum. - History of Human Knowledge
- Natural Sources
- Uses / Applications
Radio waves have an extensive range of practical applications in our daily lives. Some key uses include:
- Wireless Communication: Radio waves are the foundation of wireless communication systems, including radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. They enable the transmission of voice, data, and video over long distances.
- Radar: Radio waves are used in radar systems for navigation, weather monitoring, and military applications. Radar technology relies on the principle of emitting radio waves and detecting their reflections to determine the position and speed of objects.
- Satellite Communication: Satellites in orbit around the Earth use radio waves to transmit signals for television broadcasting, internet connectivity, weather monitoring, and global positioning systems (GPS).
- Radio Astronomy: Radio telescopes detect and study radio waves from celestial objects, allowing astronomers to explore the universe and gain insights into phenomena such as quasars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation.
- Medical Imaging: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves to create detailed images of the human body's internal structures, aiding in medical diagnoses.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites equipped with radio wave sensors monitor Earth's environment, providing crucial data for weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
The discovery and understanding of radio waves have a rich history. In the late 19th century, James Clerk Maxwell's equations🗗 provided the theoretical foundation for EM waves. It was Heinrich Hertz🗗 who first demonstrated the existence of radio waves in the laboratory in the 1880s. Hertz's experiments showed that electric sparks could produce and detect radio waves, marking a significant breakthrough.
However, it was Guglielmo Marconi🗗 who made practical use of radio waves for wireless communication in the early 20th century. His work led to the development of the first radio transmitters and receivers, paving the way for modern wireless communication systems.
Since the Big Bang radio waves have been produced by various natural sources. One of the most prominent natural sources of radio waves is celestial objects, including stars, planets, and galaxies. Radio telescopes are specialized instruments designed to observe these cosmic radio emissions, allowing scientists to study the universe's hidden secrets. Earth's atmosphere also emits radio waves through processes like lightning strikes, which generate radio signals known as sferics (sometimes also spelled "spheric"). These natural radio emissions can be harnessed for meteorological and atmospheric studies.
In conclusion, radio waves are a fundamental part of the EM spectrum with unique properties that make them indispensable for a wide range of human endeavors, from communication to scientific exploration and beyond. Their discovery and application have revolutionized how we connect, communicate, and explore the universe, making them an essential part of our daily lives and scientific endeavors.
- References:
- Wave (physical definition) Wikipedia
- Astronomical radio source (natural radio sources) Wikipedia
- Electromagnetic radiation Wikipedia
- Electromagnetic field Wikipedia
- Electromagnetic induction Wikipedia
- Maxwell's equations Wikipedia
- Heinrich Hertz Wikipedia
- Guglielmo Marconi Wikipedia
- Invention of radio (the technology) Wikipedia
- Radio (technological applications) Wikipedia
- Electromagnetic spectrum Wikipedia
- Tour of the Electromagnetic Spectrum NASA
- Radio spectrum Wikipedia
- Radio wave Wikipedia
- Radio waves UCAR
- Radio waves NASA