
 Types of radio wave propagation
Types of radio wave propagation
Radio wave propagation can occur through several mechanisms, each influencing how signals travel from the transmitter to the receiver.
Line of sight propagation (LOS): As the name suggests, this type requires a clear, unobstructed path between the transmitter and receiver. It's typical for radio waves above 70 MHz.
Ground Wave Propagation: This type occurs along the Earth's surface and is effective for medium and longwave frequencies (below 2 MHz). It's used for AM broadcasting and maritime communication.
Skywave Propagation: Here, radio waves are bounced back to Earth by the ionosphere, allowing long-distance communication. This is common in shortwave bands (3 to 30 MHz), where signals can travel around the globe. Ham radio operators and international broadcasters often utilize this method.
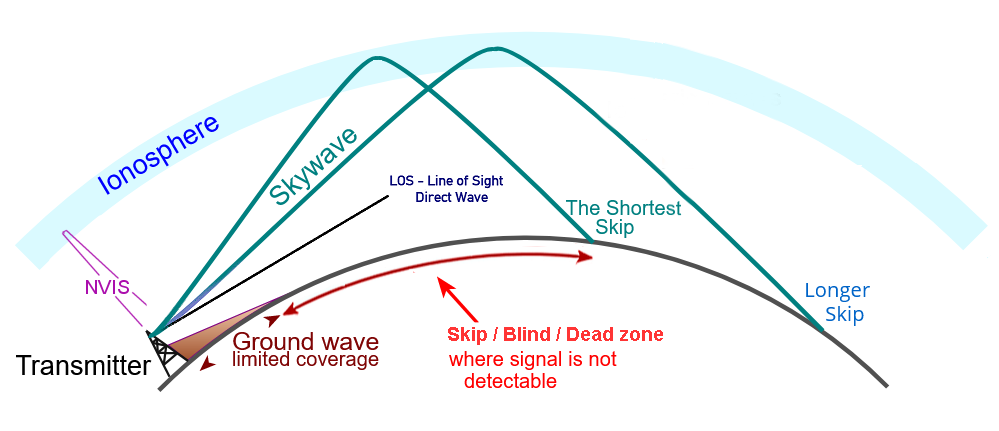 Figure 1: Illustration of "LOS," Ground Wave and "Skip" Propagation |
Tropospheric Propagation: This type relies on the troposphere, the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere, where signals can be bent or refracted. It can cause VHF and UHF signals to travel beyond the horizon, enhancing communication ranges under certain weather conditions.
 Figure 2: Troposcatter propagation |
Satellite Communication: Signals are sent to and from satellites orbiting the Earth. This type is essential for global communications, GPS, and broadcasting services.
 Figure 3: Satellite Communication |
Understanding these propagation types helps in selecting the appropriate frequencies and techniques for reliable communication.
Types of radio wave propagation
HF Radio Propagation Search Terms
Skywave propagation for hams explained
Skywave propagation for radio amateurs
What are the modes of radio propagation
What are the modes of HF radio propagation
HF propagation for hams explained
Radio propagation for hams explained