HF Propagation for Newbees
HF Propagation for Newbees
Welcome to the exciting world of HF propagation!
If you're just starting out and feeling a bit lost, don't worry. HF propagation might seem complex, but it's fascinating once you get the hang of it.
An intro to HF radio propagation
The link above will take you to another page with a basic explanation of radio waves.
If you are familiar with the basic concepts of radio waves then return back and proceed on ths page.
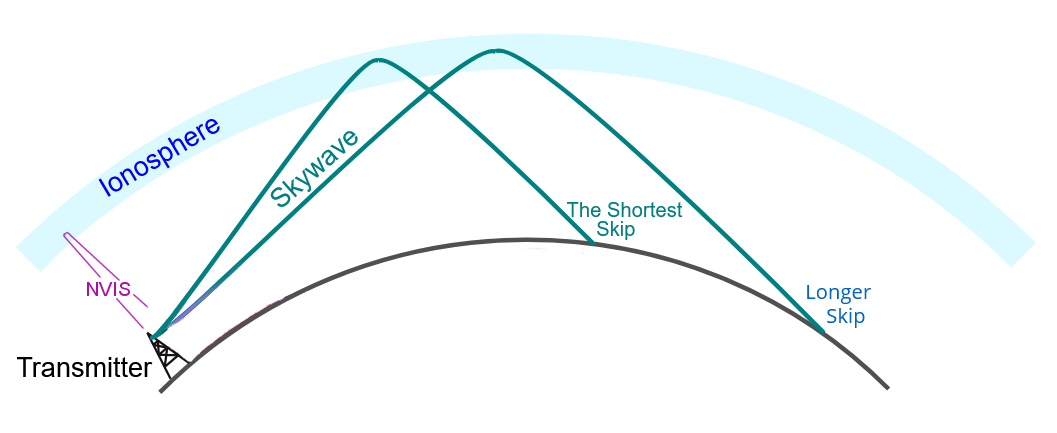
HF propagation involves the way radio waves travel across long distances by bouncing off the ionosphere.
The ionosphere is a magical region of the Earth's atmosphere that refracts radio signals, allowing you to communicate with people far away, even on the other side of the planet.
Here are a few basics to get you started:
- Sun's Role: The sun is a big player in HF propagation. Solar activity, like sunspots and flares, can make or break your communication efforts.
- Day vs. Night: HF conditions change with the time of day. At night, lower frequencies (1.8-10 MHz) work best, while higher frequencies (14-30 MHz) thrive during the day.
- Seasonal Changes: Different seasons can affect propagation. For example, you'll find better conditions on the 10-meter band during summer months.
As a newbee, make use of online resources, join radio clubs, and don't be afraid to experiment with different frequencies and times. The more you listen and learn, the better you'll understand the magic of HF propagation.