Ham Radio Propagation Overview
Ham Radio Propagation Overview
AI generated podcast courtesy of Jean-Paul Suijs, PA9X ↗
Understanding HF Propagation for Hams is critical for radio operators to plan communications and adjust equipment effectively.
- HF propagation overview
- Different HF bands have different characteristics.
- Factors affecting propagation include time of day, weather, and solar activity.
- Real-time propagation reports help understand current and forecasted conditions.
Understanding HF Radio Propagation
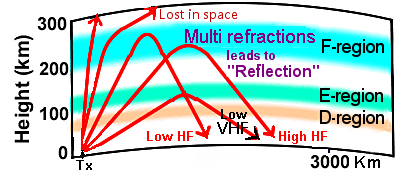
- Skywave propagation is the process of radio waves traveling through the Earth's upper atmosphere and ionosphere.
- The ionosphere is divided into D, E, and F regions, responsible for refracting radio waves back to Earth.
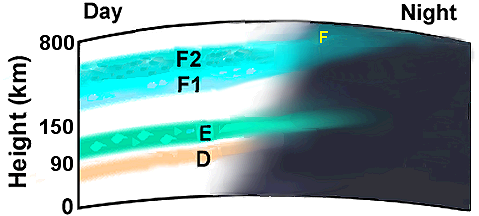
Fig. 1: Ionospheric regions - Propagation conditions fluctuate with daily, seasonal, and solar cycles.
- Daytime D region absorbs radio waves, hindering long-distance communications.
At night this region disappears, allowing E and F regions to refract radio waves.
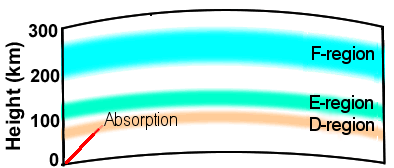
Fig. 3: D-region absorption - Solar activity, like flares and sunspots, can disrupt communications and cause signal fading (QSB).
- Extreme solar activity may cause geomagnetic storms causing radio blackouts.
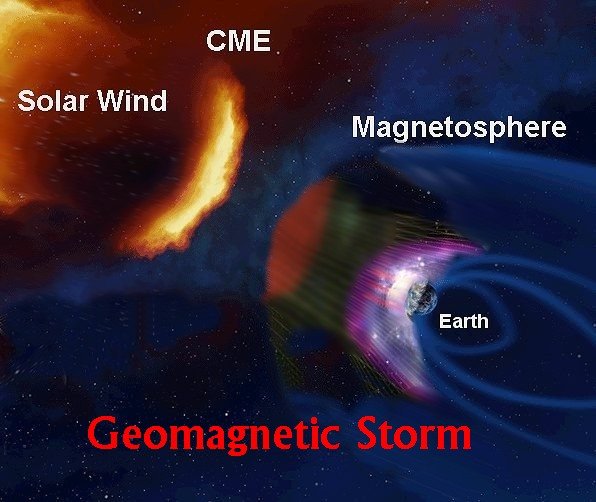
Fig. 4: Geomagnetic storm illustration

Fig. 5: Radio blackout
- A tool indicating expected conditions for radio wave propagation at a specific time and frequency.
- Used by ham radio operators to determine optimal frequencies for contacts and to track propagation changes.
- Types include ionospheric and solar flux maps.
- Popular propagation prediction tools include VOACAP, IONCAP, IPS, WWV, and WWVH.
- Generated using solar activity measurements, ionospheric soundings, and ground-based and space-based data.
- Helps in predicting contact times and frequencies, and planning for unexpected propagation changes.
Ham Radio Propagation Forecast Overview
- Ham radio propagation forecasts predict expected conditions for radio wave propagation at a specific time and frequency.
- These forecasts are used by operators to plan contacts and select optimal frequencies.
- Forecasts consider factors like solar flares, sunspot activity, and geomagnetic storms.
- Popular tools include solar flux indices and geomagnetic indices.
- Online resources like propagation prediction websites and apps provide regular, updated data.
- Some online resources use algorithms to predict propagation based on historical data and current activity.
- Weather can affect ham radio propagation, especially in VHF and UHF bands.
How Can Propagation Reports Assist Ham Radio Operators?
Ham radio operators can use propagation reports to better understand present and predicted radio wave propagation conditions.
Utilizing Propagation Reports for Ham Radio Performance
- Identifying Best Frequency Use: The report provides information on Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF) and Lowest Usable Frequency (LUF) for each band, indicating the best frequencies for long-distance communications.
- Planning for Different Time of Day: The report helps in planning for current and forecasted propagation conditions.
- Adjusting Antenna: The critical frequency for each band is provided, allowing for antenna optimization.
- Checking for Solar Flares: The report provides data on solar flux, A and K index, and sunspot number, indicating potential disruptions to communications.
- Checking for Geomagnetic Activity: The report provides information on geomagnetic activity, highlighting potential disruptions and signal fading.
- Note: These reports are forecasts and can change quickly, so a backup plan is recommended.
Top Amateur Radio Websites – Issue 2331, Aug 19, 2023
Rate this site @ DXZone |
Ham radio propagation overview
Understanding Radio Propagation
Learn High-Frequency Propagation
The Fast Track to Ham Radio Education
Beginner's guide to HF radio propagation
Understanding HAM Radio Propagation Techniques
The Fast Track to Understanding Ham Radio Propagation
Understanding of Ham Radio Propagation–You Should Know
Total visits since 17 August 2022.
Repeat visits counted as new after 24 hours.

The number of visits (graphs displayed below) peaks during HF propagation disruptions.

Visits (per day) since 2022

Visits (per day) during the last 90 days.

Visits (per day) during the last 30 days.
Hourly visits today
Repeat visits counted as new after 24 hours.
The number of visits (graphs displayed below) peaks during HF propagation disruptions.
Visits (per day) since 2022
Visits (per day) during the last 90 days.
Visits (per day) during the last 30 days.
Hourly visits today