LEARNING OBJECTIVES and NOTES
|
|
|
| Tuned Circuits 2 |
|
Understand the meaning of dynamic resistance.
Understand and apply the formula for RD given component values.
Understand the effect of damping resistors in a tuned circuit
We know that at resonance a parallel circuit has a high impedance. This is known as DYNAMIC RESISTANCE and is given the symbol RD
Also there is some DC resistance in the coil although this is not always shown on a circuit diagram for a tuned circuit.
Although the DC resistance will be very low the dynamic resistance will be very high - in the region of 50,00 ohms.
It is the dynamic resistance of a resonant parallel circuit that makes it a rejector circuit.
RD can be calculated from the following equation:
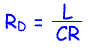
Where:
R
D = dynamic resistance
L = Inductance in Henries
C = Capacitance in Farads
R = Resistance in ohms of the inductor
NB This equation assumes that the circuit is at resonance and that the DC resistance is less than 25 ohms.
Damping resistors
In RF filters we often don't want a very sharp response
as these are difficult to tune "on the nose". What is required is a
flatter response. The way to achieve this is to add a "damping
resistor" across the circuit. The down side is that the gain of the
filter is reduced. |
Example 1

|
Recall the equivalent circuit of a crystal and that it exhibits series and parallel resonance.
These are very precise generators of
a specific frequency and are widely used in computers, radio
transmitters, and to maintain stability in frequency synthesisers.As
an alternative to using an inductor and capacitor to oscillate on a
particular frequency a quartz crystal may be used. The equivalent
circuit of a crystal is shown opposite.
Crystals will actually
oscillate on two different frequencies about 0.1% apart. One is called
the series resonant frequency. At this frequency, the crystal appears
resistive in the circuit. If capacitance is added in series with a
crystal it will oscillate at a slightly higher frequency. This is
the parallel frequency.
Manufacturers stamp one
of these two frequencies on the crystal case. When ordering a crystal
it is important to be clear if the crystal is for a series or parallel
oscillator circuit. If it is for a parallel frequency, the capacitor
required in parallel should be given by the manufacturer
|
|
Recall that voltages and circulating currents in tuned circuits can be very high and understand the implications for component rating.
You might assume that if you are
running an oscillator with a 9V supply then the components in
that oscillator should be rated at about 9V. But, as discussed in the
section on Q, the voltage and current in an oscillator can be many
times the operating voltage and current. It is therefore important that
components are rated to work at the higher voltage and currents found in resonating circuits.
|
|

