
| ADVANCED LESSON 50 |  |
| LEARNING OBJECTIVES and NOTES | |
| Antennas 2 | |
|
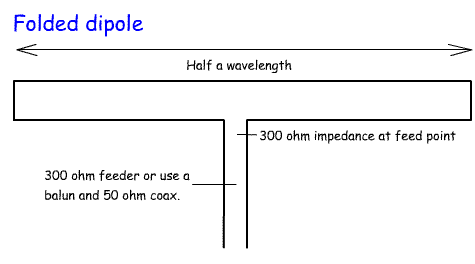
5c.4 Identify folded and trap dipoles and quad antennas in addition to those in earlier syllabuses. 5c.5 Recall that an antenna trap is a parallel tuned circuit and understand how it enables a single antenna to be resonant and have an acceptable feed-point impedance on more than one frequency. Recall that this technique may be extended to multi-element antennas such as Yagis. Revise the antenna types from Foundation Lesson 07 and Intermediate Lesson 19 The drawing shows three other types of antenna commonly used by Radio Amateurs
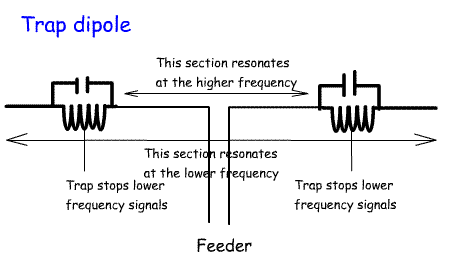
Two traps are then constructed that are tuned to have a null at 40m. These are parallel tuned circuits which have a high impedance at their resonant frequency.Traps can be made from a coil and high voltage capacitors. They can also be made from lengths of coax cable. It is important that they have a low Q to cover the band. The traps are connected to the end of the dipole. Wire is then connected to the other side of the traps on each side and adjusted to resonate on the lower band - e.g. 80m. Advantages and disadvantages of a Trap Dipole
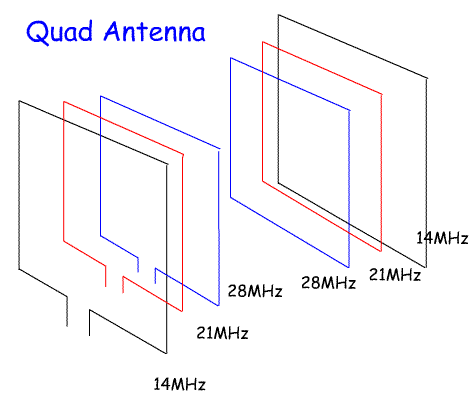
Quad antennas These consist of several full size loops mounted on a set of light weight supports. There is a separate driven element loop for each band and a separate director or reflector loop for each band. The quad antenna has a high gain and wider bandwidth than a 3 element Yagi beam. Single band quad antennas are used on 2m and 70cm where they give good gain and take up less room than a conventional Yagi. You will also need to remind yourself of the antennas mentioned in the Foundation and Intermediate syllabus. At Foundation level you had to identify the half-wave dipole, λ/4 ground plane, Yagi, end-fed wire and 5/8λ antennas. At Intermediate level recall the structure of a three-element Yagi |
   |