Understanding MUF vs. Critical Frequency
Understanding MUF vs. Critical Frequency
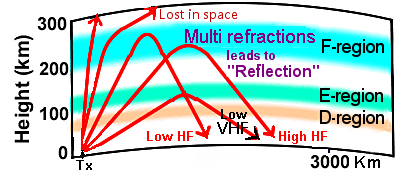
During the day, the ionospheric E and F regions refract and relflect skywaves:
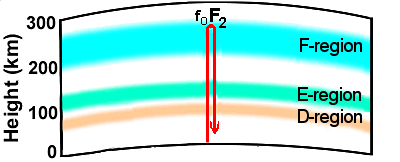
The Critical Frequency
The critical frequency ↗ (foF2 or CF) is the highest frequency below which a radio wave is refracted by the F2-region at vertical incidence, independent of transmitting power.
Calculation of fo (the plasma frequency): 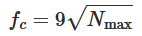 , where Nmax is the density of free electrons.
, where Nmax is the density of free electrons.
Nmax also determines the refractive index ↗ of the ionosphere: μ = √(1 - (81Nmax / fo²)) (known as the Appelton formula) ↗.
Measurement of fo: Ionosondes determine the critical frequency, which varies significantly based on location and time.
Variations of fo: The critical frequency varies with several factors: time of day, geographic latitude, season, solar activity, and geophysical conditions.
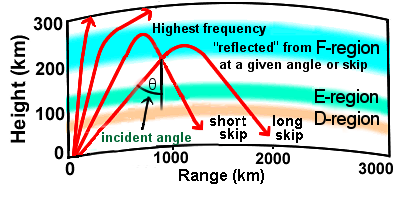
Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF) is the highest frequency that can propagate via the ionosphere under specific conditions. Frequencies exceeding MUF penetrate the ionosphere and escape to outer space, leading to a loss of communication.
The MUF is calculated using the formula:
- foF2: Critical frequency of the F2 region.
- θ: Angle of incidence relative to the vertical.
- As a rule of thumb, the MUF is approximately 3-4 times the foF2;
i.e., incident angle θ = 70°-75°; transmission angle α = 15°-20°.
For vertical incidence (θ = 0), MUF equals foF2. For oblique paths, MUF increases with sec(θ) ↗.
Factors affecting MUF:- Higher density of free electrons in the ionosphere supports higher frequencies.
- Increased solar activity raises the MUF, peaking at noon and in summer.