Sound Card Interfacing by Clint Hurd KK7UQ
Slide 1 - Introduction
Sound Card Interfacing
Slide 2 - Sound Card Interfacing - Outline
|
|
General Concept - SSB Rig & Sound Card Applications |
|
|
Sound Card Interface Requirements |
|
|
Evolution of Interface Design |
|
|
System Operation |
|
|
Common Problems and Solutions |
|
|
Example: Interfacing the FT101-E |
Slide 3 - SSB and Sound Card Applications
|
|
Combo of software, PC, sound card, SSB rig and Interface |
|
|
Software |
- Spectrum display to 5 Hz resolution
- Bandpass filter for signal - 50 Hz
- Encode/decode of signal
|
|
PC - Windows 95 or later, 100 MHz or faster |
|
|
Rig |
- SSB in either USB or LSB
- Reasonable frequency stability
- Tight filters NOT needed in most cases
- Can NOT use ALC or Compression on Transmit
- Must stay within Tx bandwidth - typically 2200 Hz or less
|
|
Interface - connects rig to the PC Sound Card |
Slide 4 - Sound Card Interface Requirements
|
|
PSK represents the "worst case" requirements |
- "Two tone" nature demands good linearity in the system - signals
must be clean to operate close to one another without interference
- Narrow bandwidth (31Hz) - can operate as close as 100 Hz apart
unless one signal is much stronger than another, or distorted
|
|
Audio from Rx to PC |
- Signal level as high as 5v p-p, typical 1v p-p
- Audio frequency range from 200 to 4000 Hz, or whatever the
transmit passband will allow
- Cables need to be shielded
- Sound card accepts max 5v p-p before saturating
- Software detects and warns against saturated signals at
about 1.5v p-p
- Several ways to control the maximum level to the sound card:
- Rx RF gain, Rx volume control, PC volume control,
Interface Rx level control
Slide 4 - Sound Card Interface Requirements
|
|
Audio from PC to Transmitter |
- Sound card output up to 5v p-p at max level - may start clipping at
around 75% level
- Rig expects microphone levels - at a level of a few millivolts up to a
hundred millivolts
- Frequency range from 200 to 4000 Hz - maximum determined by
Tx output filter bandwidth - typically around 2200 Hz
- Audio drive levels determine power output - usually rig can run at
about 50% of CW rating or less
- System must operate in an RF environment
- Shielded cables - lengths under 6 feet
- Good grounding of all components - rig, PC and tuner
- Care taken to eliminate other audio sources during transmit
Slide 5 - Sound Card Interface Requirments
|
|
SSB Rig Control |
- Tx On/Off methods:
- Manual switch
- VOX
- PTT via Serial Port Control on PC
- Tx audio drive level set by:
- Audio level from PC
- Mike gain on rig
- Attenuation, or level control potentiometer on interface
- Rx Audio to PC provided by:
- Line out
- External speaker or headset port
- Accessory port
Slide 6 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Not as simple as it first seems |
|
|
Areas that affect design |
- Linearity of all stages of Tx audio path
- Noise pickup in interface and cable system
- RF
- AC Noise (hum)
- Other sources into sound card
Slide 7 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Stage 1 - Shielded cable and resistor pad |
- Can work if:
- Cable to rig is kept short, all cables shielded
- RF environment is clean
- No common mode noise between PC and Rig
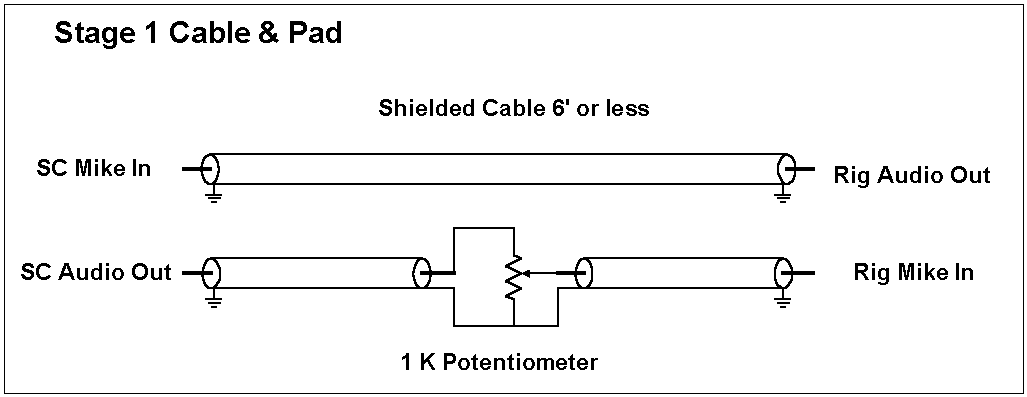
Slide 8 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Stage 2 - Isolating the Tx drive with a transformer |
- Shield grounded at Sound Card End Only
- Reduces common mode noise injection
- Can filter for RF
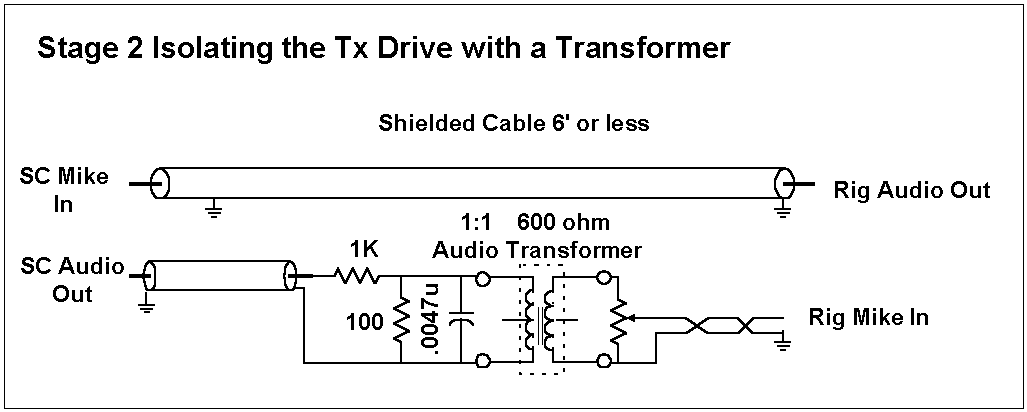
Slide 9 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Stage 3 - Complete isolation between rig and PC |
- Transformers on Tx and Rx lines
- PTT Opto/Isolated
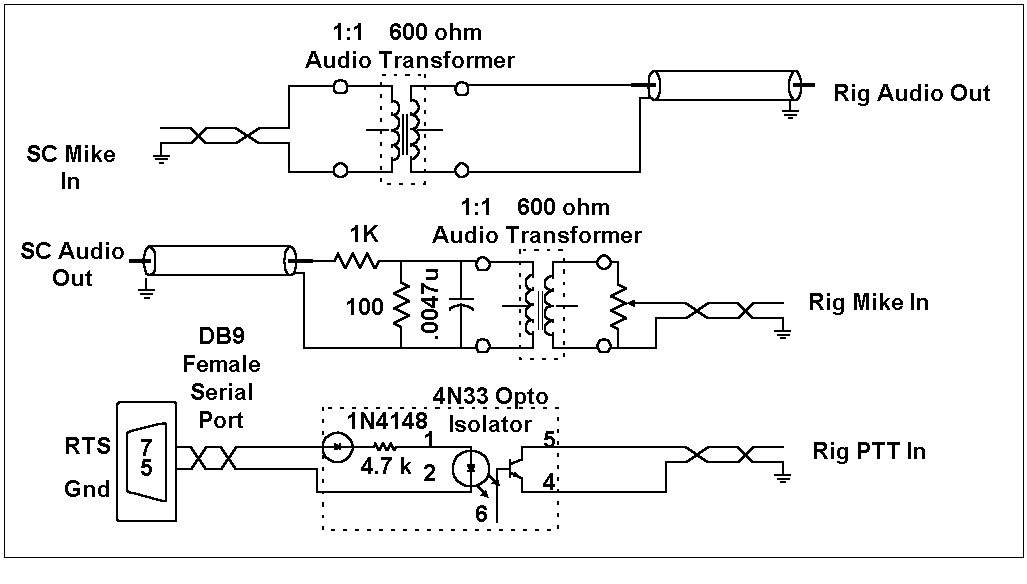
Slide 10 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Adding features to improve operability |
- Potentiometers on Tx and Rx with knobs
- Switch for PTT mode selection
- Auto (PC serial port RTS or DTR line controls)
- OFF (Disables PTT control)
- PTT ON (Forces PTT on)
- Relay for PTT for older rigs
- Capacitor on Tx drive for DC isolation
- Support for either single cable Accessory port, or two
cable mike/speaker out connection
- Switching for microphone / interface
- VOX built into interface to eliminate need for serial control
Slide 11 - Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Available interface - features and prices |
Prices are approximate, and include ALL cables needed (rig, serial port, audio cables). Prices do not include shipping and handling, or any applicable taxes. See the manufacturers website for their latest pricing and products.
Ready to Go
|
|
Rascal $49 BuxComm http://www.packetradio.com/psk31.htm |
Tx path transformer
Rx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
LED for PTT
Supports mike/ext.spkr or single cable accessory connection
|
|
Nomic $58 West Mountain Radio http://www.westmountainradio.com/ |
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
|
|
Signal Link SL-1 $60 Tigertronics http://www.tigertronics.com/ |
Tx path transformer
Rx path transformer
LED for "PTT"
May require external power
Switch for PTT mode
VOX built into interface
|
|
Rigblaster $100 West Mountain Radio http://www.westmountainradio.com/ |
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
Relay for PTT
LED for PTT
Requires external power (included)
Mike switching built in
Mike PTT interrupt to software
|
|
Rigblaster Plus $130 West Mountain Radio http://www.westmountainradio.com/ |
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
Relay for PTT
LED for PTT
Requires external power (included)
Mike switching built in
Mike PTT interrupt to software
CW/FSK keying output
Jack for foot switch PTT
Home built Projects
|
|
Rascal kit $25 BuxComm http://www.packetradio.com/psk31.htm |
Tx path transformer
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
LED for PTT
Supports mike/ext.spkr or single cable accessory connection
|
|
K8CAV Design (from QST) estimated part cost $35 |
Tx path transformer
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
Potentiometers for Tx and Rx level control
Supports mike/ext.spkr or single cable accessory connection
|
|
kk7uq -01 $55 Discovery Bay Computing http://www.waypoint.com/users/~discobay/ |
Tx path transformer
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
Potentiometers for Tx and Rx level control
Relay for PTT
LED for PTT indication
PTT mode switch
Requires external +13.8v power
Supports mike/ext.spkr or single cable accessory connection
|
|
kk7uq -02 $50 Discovery Bay Computing http://www.waypoint.com/users/~discobay/ |
Tx path transformer
Tx path transformer
Opto isolated PTT
Potentiometers for Tx and Rx level control
LED for PTT indication
PTT mode switch
Supports mike/ext.spkr or single cable accessory connection
Slide 12 Evolution of Interface Design
|
|
Schematic of kk7uq Sound Card Interface |
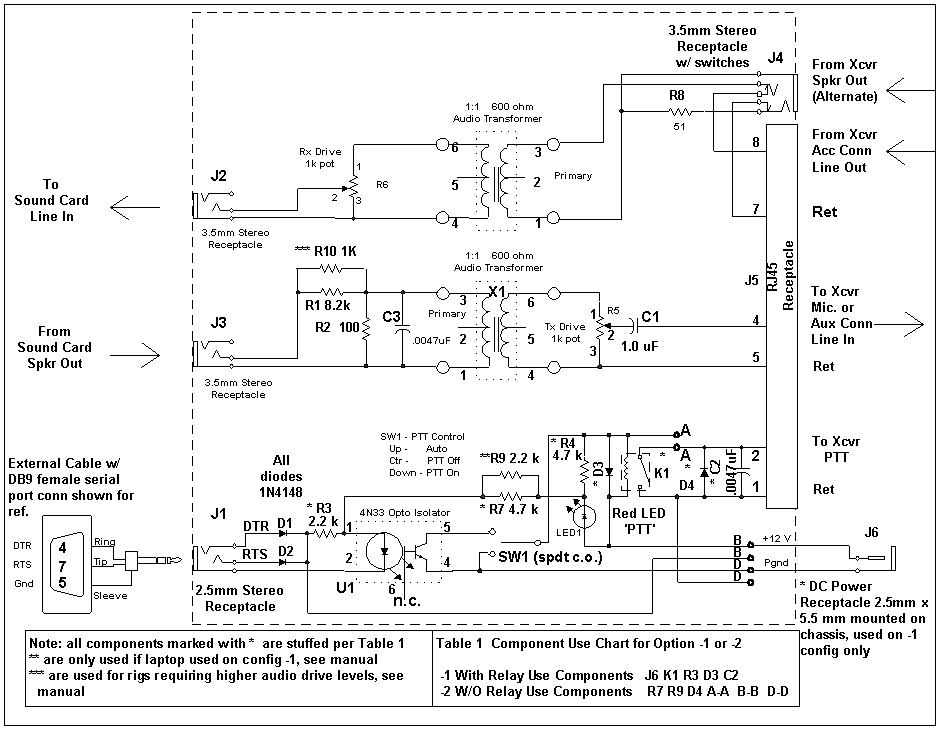
Slide 13 System Requirements
|
|
Grounding - of computer, rig, antenna tuner is a must |
|
|
Transmit |
- Absolute frequency control is not necessary
- Frequency stability is more important
- You MUST say within the Tx audio passband on transmit
- Be able to monitor your output level and ALC
|
|
Receive |
- Use RF gain as your primary level control for receive
- Tune the base frequency so the signal you want to work is in the range
of 1000 to 2000 Hz
Slide 14 System Requirements
|
|
IMD Measuring |
- IMD (Inter-Modulation Distortion) measurements are a part of most software
for PSK31
- Measures the signal level of the fundamental signal and it's harmonic. Represented
in -db from fundamental level
- A good IMD is -24db
- On strong signals, reduce the RF gain, or else the IMD measurment will read low.
- If signals are weak, or QRN level is high, measurements will read lower than they
really are
- There are some small differences in IMD readings between the popular software
packages, maybe within a 6db spread
|
|
Dealing with Strong Local Signals |
- Can live without a narrow filter ... but ... if you have one, use it with your passband
tuning to reduce the signal level of the offending signal - this will reduce the effect
of AGC pumping
Slide 15 System Requirements
Software available
Digipan http://www.digipan.net/
Has an internal log which supports name & qth pop on subsequent qso.
Has waterfall display that covers 4000 Hz
Monitors two channels
Modes supported: PSK31 (BPSK and QPSK)
Written by KH6TY, UT2UZ, UU9JDR
Hamscope http://www.qsl.net/hamscope/
Supports YPLOG
Has both waterfall and spectrum displays that cover 2800 Hz
Monitors two channels
Supports PSK31 (BPSK & QPSK); MFSK16; RTTY; CW
Written by KD5HIO
Helleschreiber http://iz8bly.sysonline.it/
Internal log
Supports PSK31 (BPSK & QPSK), Hellschreiber
Written by IZ8BLY
MMSSTV
http://www.qsl.net/mmhamsoft/Internal log
Supports SSTV
Written by JE3HHT, who also wrote MMTTY
MMTTY http://www.qsl.net/mmhamsoft/
Internal log, supports name and qth pop on subsequent qso, has contest mode
Supports RTTY
Considered the best sound card implementation of RTTY available as freeware,
Both Hamscope and Zakanaka use the MMTTY engine for their RTTY modes
Written by JE3HHT
MixW
http://www.mixw.net/Internal log which supports name and qth pop on subsequent qso.
Supports PSK31 (BPSK &QPSK), MFSK, RTTY, Hellschreiber, Throb, SSTV and many more
Demo versions are available for no charge, but the registered version is a for fee product
Written by UT2UZ, who also wrote Digipan
Stream http://iz8bly.sysonline.it/
Internal log
Supports MFSK8, MFSK16 and PSK31 modes
Written by IZ8BLY
WinPSK http:/www.qsl.net/ae4jy/
Supports PSK31 (BPSK & QPSK)
Written by AE4JY.
This was one of the first Windows supported PSK programs. Moe, AE4JY developed
the PSKCORE engine to provide the DSP algorithms required to implement PSK31.
The PSKCORE engine is also used by WinPSK, WinWarbler, Hamscope and Zakanaka.
WinWarbler http://www.qsl.net/winwarbler/
Supports PSK31 (BPSK &QPSK)
Monitors three channels
Written by AA6YQ
WinWarbler is a member of the DXLab suite of interoperating applications, which
provide logging, QSL card/label generation, transceiver and rotor control,
propagation prediction, DX cluster spot collection/analysis and real-time mapping
of the solar terminator, beam headings and DX spots. See www.qsl.net/dxlab
for more details on this suite.
Zakanaka http://www.qsl.net/kc4elo/
Has excellent support of the Logger program written by the same author.
Supports PSK31 (BPSK & QPSK), RTTY (using MMTTY engine)
Written by K4CY
Slide 16 Common Problems & Solutions
|
|
Wide Signal |
- Overdrive of audio on Tx
- ALC or Compression ON during Tx
|
|
Hum on Signal |
- Needs shielding on cables
- Common mode noise, use transformers on both channels
- Ground all system components to a good earth ground
|
|
Harmonics of Audio Carrier |
- ALC on, or Compression On
- Transmitting outside of Tx bandpass area
- Transmitting too low in the waterfall
|
|
Frequency Offset Between Stations |
- RIT or XIT is ON, turn it OFF
- One of the transmitters has an offset in their transmitter or receiver
one stations should turn NET OFF, and freeze their Tx frequency, the
other should leave NET ON.
|
|
Signal Cutting In and Out |
- CPU too slow for the processing required
- Too many process running on CPU while actively processing psk signals
- VOX is set too close to the signal level
- Bad connection
|
|
Strange Signals Mixed with a Good PSK Signal |
- Mute all sources on "Playback" except WAVE and Volume Control
|
|
Sounds from the Shack Being Transmitted |
- Sounds such as typing, phone ringing etc.
- Mike is active, disconnect it
- Mike in PC is active, mute it
See Sound Card Interface Manual Section 7 for setup and trouble shooting procedures
Slide 17 Example: Interfacing the FT 101 E
|
|
Classic Tube/Solid State Rig |
- No Accessory Port available
- No line out
- Frequency accuracy is an issue
- Stability may be an issue
- No +13.8v supply available, power supply is internal to the rig
- PTT is at +13.8v when not activated, draws 120 ma. when activated
|
|
PC is a Laptop |
- Only on serial port is available
- Mike input is a 3.5mm stereo connector on the front of the PC
- Headset output is a 3.5mm stereo connector on the front of the PC
- Serial port signal levels may be lower than standard
|
|
Solution |
- Use 4 pin screw on mike connector for Tx audio, and PTT
- Use headset out for Tx audio, use a Y connector if want to monitor audio
- Use kk7uq -01 (with relay for PTT) design
Dual transformers
Opto isolated PTT drives reed relay for PTT contact closure
Interface has level control potentiometers for tx and rx level settings
Use Hamscope for software (ease of use, multiple modes)
Use wall wart supply to power reed relay
Increase drive level of opto isolator because of lower than RTS signal
|
|
Performance |
- Frequency setting done by observing signals in 14.070 area and resetting dial on rig
- Transmit level of 25 to 50 watts was used
- Good reports on audio quality - IMD of -30db or better
- Some drift - about 30Hz in a one minute over
Other station "locked" his Tx freq so could return to the starting point each time
- Contacts
First contact was XE1L in Mexico City
Second contact was VK2KUI Yarrahapinni in New South Wales
Made ten contacts in the TARA Rumble PSK contest
|
|
Conclusion |
- A useable rig for PSK, some care must be taken when dealing with the drift issue.