It’s the system generally used.
The railway tie can be wooden, flange steel or reiforced concrete; these lasts
are still in rehearsal period in some countries from Europe, Asia and Australia.
Crossbeam wooden:
They are used where the steel could be spoiled by the humidity and/ or
atmospheric agents, or when the signal circuit demand an isolation between the
different roads tracts.
Comparative report
Crosstie
wooden treatise
The railway tie must come
from healthy wood, that not present holes produced by wood destroyer insects,
without fissures produced by freezing, holes coming from branches in rot or
stumps of swollen branches; neither be bent.
They musn’t
have plug holes, or branches or any mold or mushrooms formations.
The “Haya”
railway tie can have a red small core ( up to 1/ 6 of the cross section ) when
they’re on the inferior layers.
Big cracks are not admitted (
more than 30 cm depth ).
The wood must
be cut beginning the sap movement.
The wood for
evergreen oak railroad must be cut within 18 to months
the supply and the “Haya” one within
9 months.
Railroads must be worked in the
way that superior and inferior surfaces could be most parallel to the wood
fiber.
It cannot use wild evergreen oak
wood’s railway tie.
I. Railroads of 1st
class line.
III. Railroads of change
of line
L= 2,70m;
b= 0,26m; h= 0,16m;
L = 3 to 4m; b=
0,26m; h= 0,16m;
IV.
Railroads of 3th class line
II. Railroads of 2nd
class line.
L = 2,50m;
b= 0.20 to 0,22m;
L= 2,50m;
b= 0,24m; h= 0,14m;
h= 0.14 to 0,15m;
Railway tie must have no more than 2 cm of bark tree. Cut time is between
May 15 and August 15. Railroads will be heaped on wedges to not be in
touch with floor.
The supply doesn't include impregnation neither treatment.
Railway tie
manufactured with Hütte: (
"Centennial")
The "Centennial” railway tie, replace to the wooden railway tie
with many advantages, on the
demanded by the measured and supplies norms, and they don't require impregnation
neither treatments.
Hütte offers the railway tie of section and longitude according to the mechanical stress. The same as the railway tie of reinforced concrete, the manufactured with hütte, could go seated on stone ballast or directly leaning on the subgrade, because of their properties ( absorption 0, inert to the insects and hydrocarbons chemical).

Wood screw:
They press the rails skate , already directly (fig.33), or by means of
staples (fig.42), already by means of wedges (fig.43); the Austrian Railways
have used with success the Hohenegger badges (fig.47) , useful width (in
Germany): 120, 150, and 180 mm.; core diameter 16 mm. for under, the head
profile corresponds to that of the rail or is horizontal if it is pressing on a
staple.
Drill diameter , for railway tie manufactured with Hütte material
(Centennial) must be one less milimeter to the thread core.
Fixation of the rail to the wooden railway tie
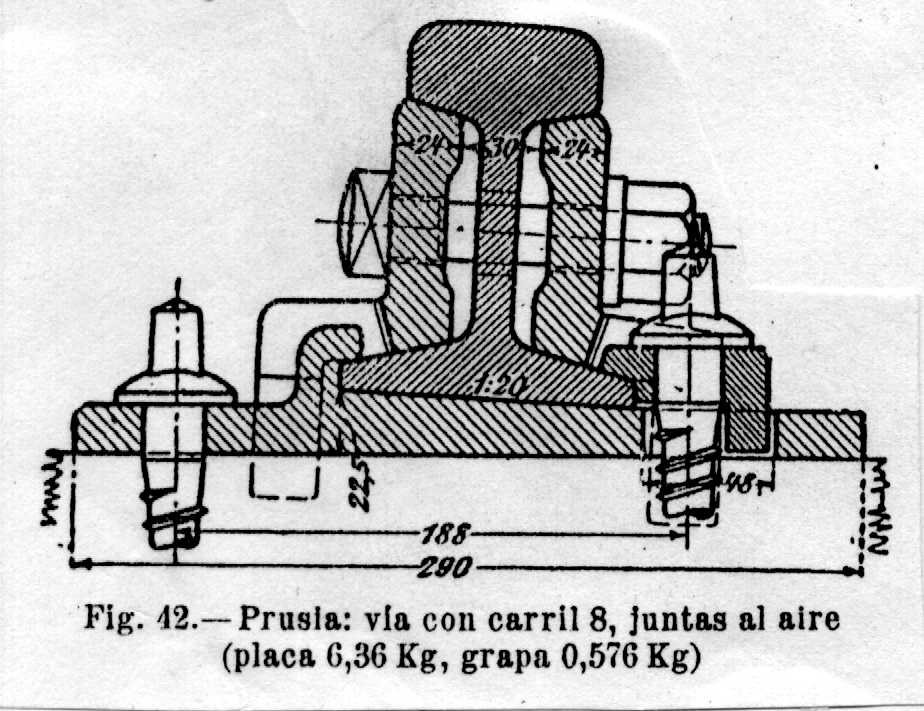
Seat badges
:
At the beginning the rails went directly leaning on the railway tie,
mortising these in order to give those the inclination of 1: 20; this system has
the defect that the rail movements quickly polish the railway tie (mainly if
they are soft wooden) destroying them.
The most using today, is to hold the rails to rectallies badges, that
increase the support surface (dividing better the load) and they
distribute the traverse pushes between all the fixation elements, reducing the
railway ties fatigues.
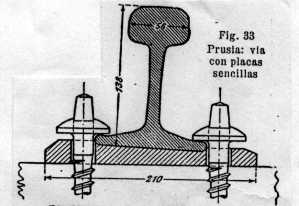
The open seat badges (fig.34), have been used during much time and they join to the railway tie with the same wood screw that hold the rail. In Spain seat badges of this are used but of uniform thick (fig.41); the rail inclination toward inside, is mortising achieved (1: 20) the wooden railway tie.
Seat badges
with claw:
They’re in the internal and external side of the line and they have
staple of vertical pressure in the opposed side. Defect: the initial game
between the skate and the claw, that increase with the natural waste, finish the
retainer action of the claw; thus increases the staple fatigue
and their wood screw, that they slaken off and they favor the rail slip.
The figure 48 represents the badge model of claw for rail 15c, new model
with staples; system that avoid the lateral pushes and it reduce the waste but
it doesn't impede to the rail get up. The perfect rail fixation, vertical and
horizontal, just can be reached
if the rail is fixed with independent elements of the ones that hold the badge,
how it happens to the English rails of double mushroom supported in bearings
(fig.44 to 46).
The system adopted by the "German Railroads" in their current
type of line (fig.48) fulfil both requirements (using it also other
administrations). In the tunnels, some German railroads use today the vignole
rail on bearings (fig.45).
Home Spanish Italian Advantage Testing Description Ecology Railway tie Comments