|
Calibration:
The tool I used to calibrate the watt meter is
a DC volt meter, like a digital mulit-meter. A volt source of 24 v DC and
a good 10K ohm potentiometer.
The theory of calibration:
The formula for RF Watts or power is P=E*I.
In our case, we are looking for the peak volt for an X watts with a constant
load of 50 ohms.
P=E(Sq)/R or E=(Sq Rt.) P R
(Note: I used a 500 uA meter from which
I removed the scale, re-painted it white, then drew a base line arc with
marks for zero and max.)
The next step was to calculate a table of
peak volts in relation to the units of Watts. Remember, the scale will
not be linear. It will be a logarithmic scale compressing on the high end.
On a scale of 0-5, One will be about midway. Because we have a peak-reading
volt meter, and the power formula is RMS volts, we use Ep=Ea*1.414 (Where
Ep=Peak and Ea= average)
to find E for calibrating the scale.
The following is an example for the 5W level:
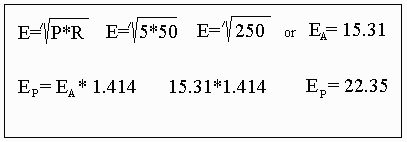
|
|