Parallel code search is a technique that uses FFT to find correlation. You only have to search in 41 frequency-bins. The following program is used:
package parCodSearch;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import util.RingBuffer;
import src_old.Complex;
import util.FileIO;
import util.GoldSequence;
import util.ShowPlot2d;
import DSP.InplaceFFT;
public class Engine extends Component {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
FileIO myFile;
String file = "params.dat";
private int readParam(String var) {
int result = myFile.readParam(var, file);
myFile.log(var + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public void parCodSearch() {
/*
* parallel code phase search acquisition Kees de Groot 2009 / 2010 /
* 2011
*
* input: file params.dat with all necessary parameters data-file with
* samples of a real GPS-receiver
*
* output: file ParCodSea.dat outputdata PRN and frequency
*
* algorithm: for PRN's and freq's: calculate PRN-sequence Fourier
* transform complex conjugate multiply samples with quadrature local
* oscillator create complex input-signal Fourier transform multiply:
* fft(inp) * fft(prn) inverse FFT search maximum
*/
String myName = "parCodSearch";
String version = "3.3";
myFile = new FileIO();
myFile.FileSetup("ParCodSea.dat");
myFile.log("/ " + myName);
myFile.log("version = " + version);
myFile.log("/ parallel code phase search acquisition");
myFile.log("/ take exactly 1 msec worth of samples");
myFile.log("/ calculate maximum for all PRN's");
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
double time1 = cal.getTimeInMillis();
DateFormat ff = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,
DateFormat.MEDIUM);
Date now = cal.getTime();
myFile.log("starttime = " + ff.format(now));
double fSample = readParam("fSample");
double ts = 1 / fSample;
double mFreq = readParam("mFreq");
int numSam = (int) Math.floor(1E-3 / ts); // 1 msec worth of samples
myFile.log("numSam = " + numSam);
// calculate nearest bigger power of two
int npower2 = 1;
while (npower2 <= 2 * numSam - 1) {
npower2 = 2 * npower2;
}
myFile.log("npower2 = " + npower2);
int inputSamples[] = new int[numSam];
// read 1 msec worth of samples
for (int k = 0; k < numSam; k++) {
inputSamples[k] = myFile.readByte();
}
Complex[] IQ = new Complex[npower2];
double result[] = new double[npower2];
// Complex[] prnBufferSaved = new Complex[npower2];
int PRNstart = readParam("PRNstart");
int PRNstop = readParam("PRNstop");
int fdeltastart = readParam("fdeltastart");
int fdeltastop = readParam("fdeltastop");
int criterion = readParam("criterion");
double fmax = 0;
for (int PRN = PRNstart; PRN <= PRNstop; PRN++) {
myFile.log("PRN = " + PRN);
// calculate a code-sequence
// create a buffer with 1023 samples of PRN
RingBuffer prnRingBuf = new RingBuffer(1023);
GoldSequence myGoldSequence = new GoldSequence(PRN);
for (int i = 0; i < 1023; i++) {
int sample = myGoldSequence.nextan();
prnRingBuf.write(sample);
}
// create a prn-buffer with same length as IQ
Complex[] prnBuffer = new Complex[npower2];
// fill this buffer with prn-code-sequence
for (int ti = 0; ti < numSam; ti++) {
double t = ti * ts;
prnBuffer[ti] = new Complex(prnRingBuf.getPrnP(t), 0);
}
// pad with zero-valued samples
for (int ti = numSam; ti < npower2; ti++) {
prnBuffer[ti] = new Complex(0, 0);
}
InplaceFFT.fft(prnBuffer);
// complex conjugate
for (int i = 0; i < prnBuffer.length; i++) {
prnBuffer[i] = prnBuffer[i].conjugate();
}
double max = 0;
int imax = 0;
for (int fdelta = fdeltastart; fdelta <= fdeltastop; fdelta = fdelta + 500) {
double f = mFreq + fdelta;
for (int ti = 0; ti < numSam; ti++) {
double t = ti * ts;
double arg = 2 * Math.PI * f * t;
IQ[ti] = new Complex(Math.cos(arg) * inputSamples[ti], Math
.sin(arg)
* inputSamples[ti]);
}
// pad with zeroes
for (int ti = numSam; ti < npower2; ti++) {
IQ[ti] = new Complex(0, 0);
}
// Fourier transform IQ
InplaceFFT.fft(IQ);
// multiply: fft(inp) * fft(prn)
for (int i = 0; i < prnBuffer.length; i++) {
IQ[i] = IQ[i].times(prnBuffer[i]);
}
// inverse FFT
InplaceFFT.ifft(IQ);
// calculate maxima
double average = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = IQ[i].abs();
average += result[i];
if (result[i] > max) {
max = result[i];
imax = i;
fmax = f;
}
}
average /= result.length;
if (max / average > criterion) {
myFile.log("PRN = " + PRN);
myFile.log("fdelta = " + fdelta);
myFile.log("\t" + "max = " + max);
myFile.log("imax = " + imax);
myFile.log("max/average = " + (int) (max / average));
}
}
myFile.log("max = " + (int) max);
myFile.log("imax = " + imax);
myFile.log("freqmax = " + (int) fmax);
}
cal = Calendar.getInstance();
now = cal.getTime();
double time2 = cal.getTimeInMillis();
myFile.log("stoptime = " + ff.format(now));
double dif = time2 - time1;
myFile.log("runtime = " + dif + " (msec)");
}
}
|
The output in file ParCodSea.dat:
/ data\ParCodSea.dat / Creation date/time 15-feb-2011 13:32:22 / parCodSearch version = 3.3 / parallel code phase search acquisition / take exactly 1 msec worth of samples / calculate maximum for all PRN's starttime = 15-feb-2011 13:32:22 fSample = 38192000 mFreq = 9550000 numSam = 38192 npower2 = 131072 PRNstart = 14 PRNstop = 27 fdeltastart = -10000 fdeltastop = 10000 criterion = 80 PRN = 14 max = 3221 imax = 129405 freqmax = 9554500 PRN = 15 max = 9572 imax = 129200 freqmax = 9550000 PRN = 16 max = 3208 imax = 3178 freqmax = 9556000 PRN = 17 max = 3270 imax = 3461 freqmax = 9553500 PRN = 18 max = 5418 imax = 113601 freqmax = 9548500 PRN = 19 max = 3340 imax = 125521 freqmax = 9554500 PRN = 20 max = 3243 imax = 4272 freqmax = 9547000 PRN = 21 max = 6736 imax = 13403 freqmax = 9547500 PRN = 22 max = 8737 imax = 6284 freqmax = 9549500 PRN = 23 max = 3454 imax = 1956 freqmax = 9555000 PRN = 24 max = 3445 imax = 5855 freqmax = 9544500 PRN = 25 max = 3792 imax = 1462 freqmax = 9547500 PRN = 26 max = 4610 imax = 119705 freqmax = 9545000 PRN = 27 max = 3487 imax = 8990 freqmax = 9557000 stoptime = 15-feb-2011 13:41:01 runtime = 518921.0 (msec)
The most promising PRN is obviously:
PRN = 15 max = 9572 imax = 129200 freqmax = 9550000
With a small alteration of the program a picture of PRN = 15 can be plotted in 3d. The picture will show all correlations for all frequencybins for PRN = 15 only. The program:
package parCodSearch1;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import util.RingBuffer;
import src_old.Complex;
import util.FileIO;
import util.GoldSequence;
import util.ShowPlot;
import util.ShowPlot3d;
import DSP.InplaceFFT;
public class Engine extends Component {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
FileIO myFile;
String file = "params.dat";
private int readParam(String var) {
int result = myFile.readParam(var, file);
myFile.log(var + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public void fillArray31() {
double[][] plotData3d;
// parallel code phase search acquisition
// with 3d-display
myFile = new FileIO();
myFile = new FileIO();
myFile.FileSetup("ParCodSea1.dat");
myFile.log("version = 1.0");
myFile.log("/ parallel code phase search acquisition");
myFile.log("/ take exactly 1 msec worth of samples");
myFile.log("/ calculate and show 3d-display");
int PRN = readParam("PRNstart");
int fdeltastart = readParam("fdeltastart");
int fdeltastop = readParam("fdeltastop");
myFile.log("PRN = " + PRN);
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
double time1 = cal.getTimeInMillis();
DateFormat ff = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,
DateFormat.MEDIUM);
Date now = cal.getTime();
myFile.log("starttime = " + ff.format(now));
double fSample = readParam("fSample");
double ts = 1 / fSample;
double mFreq = readParam("mFreq");
int numSam = (int) Math.floor(1E-3 / ts); // 1 msec worth of samples
// calculate nearest bigger power of two
int npower2 = 1;
while (npower2 <= 2 * numSam - 1) {
npower2 = 2 * npower2;
}
myFile.log("npower2 = " + numSam + " npower2 = " + npower2);
int inputSamples[] = new int[numSam];
// read 1 msec worth of samples
for (int k = 0; k < numSam; k++) {
inputSamples[k] = myFile.readByte();
}
/*
* multiply samples with local oscillator for all 41 frequencies and
* form complex input-signal for the Fourier transform
*/
Complex[] IQ = new Complex[npower2];
double result[] = new double[IQ.length];
int plotnum = 1024;
int zf = npower2 / plotnum; // zoomfactor for display
int numfs = 41;
plotData3d = new double[numfs][plotnum];
double max = 0;
int imax = 0;
int fnummax = 0;
{
// calculate a code-sequence
// create a buffer with 1023 samples of PRN
RingBuffer prnRingBuf = new RingBuffer(1023);
GoldSequence myGoldSequence = new GoldSequence(PRN);
for (int i = 0; i < 1023; i++) {
int sample = myGoldSequence.nextan();
prnRingBuf.write(sample);
}
// create a prn-buffer with same length as IQ
Complex[] prnBuffer = new Complex[IQ.length];
// fill this buffer with prn-code-sequence
for (int ti = 0; ti < numSam; ti++) {
double t = ti * ts;
prnBuffer[ti] = new Complex(prnRingBuf.getPrnP(t), 0);
}
// padd with zero-valued samples
for (int ti = numSam; ti < npower2; ti++) {
prnBuffer[ti] = new Complex(0, 0);
}
// fft
InplaceFFT.fft(prnBuffer);
// complex conjugate
for (int i = 0; i < prnBuffer.length; i++) {
prnBuffer[i] = prnBuffer[i].conjugate();
}
for (int fdelta = fdeltastart; fdelta <= fdeltastop; fdelta = fdelta + 500) {
int fnum = (fdelta + 10000) / 500;
System.out.print(fnum + ",");
if (fnum == 30) {
System.out.println();
}
double f = mFreq + fdelta;
for (int ti = 0; ti < numSam; ti++) {
double t = ti * ts;
double arg = 2 * Math.PI * f * t;
IQ[ti] = new Complex(Math.cos(arg) * inputSamples[ti], Math
.sin(arg)
* inputSamples[ti]);
}
// pad with zeroes
for (int ti = numSam; ti < npower2; ti++) {
IQ[ti] = new Complex(0, 0);
}
// Fourier transform IQ
InplaceFFT.fft(IQ);
// multiply: fft(inp) * fft(prn)
for (int i = 0; i < prnBuffer.length; i++) {
IQ[i] = IQ[i].times(prnBuffer[i]);
}
// inverse FFT
InplaceFFT.ifft(IQ);
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = IQ[i].abs();
if (result[i] > max) {
max = result[i];
imax = i;
fnummax = fnum;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < plotnum; i++) {
double acc = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < zf; j++) {
acc = acc + result[zf * i + j];
}
plotData3d[fnum][i] = acc;
}
}
}
int id = 1;
String title = "peak PRN = " + PRN;
ShowPlot myPlot = new ShowPlot(id, plotData3d, title);
myPlot.showFigure();
System.out.println();
myFile.log("max = " + max);
myFile.log("imax = " + imax);
myFile.log("fnum = " + fnummax);
// int fnum = (fdelta + 10000) / 500;
int fdelta = fnummax * 500 - 10000;
myFile.log("fdelta = " + fdelta);
double f = mFreq + fdelta;
myFile.log("f = " + f);
cal = Calendar.getInstance();
now = cal.getTime();
double time2 = cal.getTimeInMillis();
myFile.log("stoptime " + ff.format(now));
double dif = time2 - time1;
myFile.log("runtime (msec): " + dif);
}
}
|
the output in ParCodSea1.dat shows:
/ data\ParCodSea1.dat / Creation date/time 21-feb-2011 22:01:40 version = 1.0 / parallel code phase search acquisition / take exactly 1 msec worth of samples / calculate and show 3d-display PRNstart = 15 fdeltastart = -10000 fdeltastop = 10000 PRN = 15 starttime = 21-feb-2011 22:01:40 fSample = 38192000 mFreq = 9550000 npower2 = 38192 npower2 = 131072 max = 9572.72594206364 imax = 129200 fnum = 20 fdelta = 0 f = 9550000.0 stoptime 21-feb-2011 22:02:18 runtime (msec): 38443.0
The corresponding picture is:
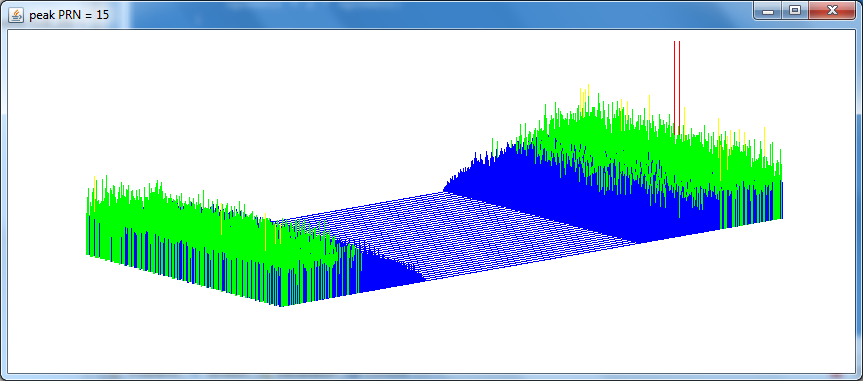
Discussion
imax = 129200 and there are 38192 bins. So the peak is at 38192 - 129200 = 1872 samples before the first sample.