7470.EXE is a Win32-based emulator for the HP 7470A plotter. It will acquire an HP-GL/2 plot and render it in a window. The plot can then be printed, viewed as an overlay with other plots, or saved in several different graphics file formats as well as its original HP-GL/2 format.
With the help of 7470.EXE, you can capture screenshots from GPIB-based test equipment such as digital oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, and more. 7470.EXE can even recognize certain instrument models and and request plots from them without user access to their front-panel controls.
7470.EXE is part of the KE5FX GPIB Toolkit. The latest version of the Toolkit is downloadable here.
Running 7470
Depending on the options you selected during installation, you can run 7470.EXE from the Start menu, by clicking on its desktop shortcut, or by using its Quick Launch icon on the taskbar. You can also run 7470.EXE from a DOS-box command line or Windows Start->Run... command, optionally specifying a GPIB address from which to acquire host-requested plots (see below), or the names of one or more existing HP-GL/2 data files. Use quotes around filenames that contain spaces - for example,
7470 "IMD test.plt" ... Display "IMD test.plt" by itself
7470 before.plt after.plt ... Overlay before.plt and after.plt
7470 (no command-line options) ... Display all plots in the current directory
You can acquire your own HP-GL/2 .PLT files via the options on the Acquire menu, if your PC has a National Instruments-compatible GPIB interface or a Prologix USB-GPIB adapter. It's important to understand that there are two ways to do this in 7470.EXE. Unlike other plotter emulators, 7470.EXE supports both host-requested and device-initiated plotting operations.
Host-Requested Plots
A few instruments, currently limited to the following models, support "host-requested" plotting in 7470.EXE.
If you have a National Instruments-compatible GPIB adapter, you'll normally issue host-initiated plot requests by selecting one of the "Request plot from supported device at address n" selections on the Acquire menu. Prologix GPIB adapter users should review the comments in SERIAL.INI carefully to learn how to configure the Toolkit applications for use with the available Prologix adapter versions. Note that earlier Prologix adapters, and those with their DIP switches set to Device mode, can't support host-requested plots at all.
Most instruments that support host-requested plots may be addressed directly on the 7470.EXE command line, just like a .PLT filename:
7470 3
The above example is suitable for inclusion in a Windows desktop shortcut. When clicked, the shortcut will launch 7470.EXE, which will then immediately request
a plot from the supported instrument at GPIB address 3. This feature allows you to capture screenshots with a single mouse click on the host PC.
Host-Requested Plots via Instrument Menu Shortcuts
Beginning with the 1.80 release of 7470.EXE, you can also add strings of the form
instrument_0 Tektronix 2430A at GPIB address 4\tF2
to the 7470.INI file in the 7470.EXE program directory. The file contains several commented-out entries that illustrate how
this is done. (See below for more information on 7470.INI.) If any of these "instrument_" lines are present in 7470.INI,
the Acquire menu won't contain its usual list of GPIB-address entries. Instead, the Acquire menu will present a list of the instrument
name/address specification strings from 7470.INI and allow you to select one with the mouse, or, alternatively, by
pressing a function key.
Important note for HP 8566A/8567A/8568A users
These analyzers can't be automatically identified and addressed by 7470.EXE, and they also don't support HP-GL/2 plotting. Never fear, though... 7470.EXE can still work with them. To acquire screenshots from an HP 8566A, 8567A, or 8568A, you must create an instrument menu shortcut to tell 7470.EXE you're accessing one of these spectrum analyzers.
In order to tell 7470.EXE to access one of these analyzers, the instrument name portion of the 7470.INI menu-shortcut
entry must contain the string "8566A", "8567A", or "8568A". When the instrument name contains one of
these model identifiers, 7470.EXE will request raw annotation, state, and trace data from the analyzer and
generate its own HP-GL/2 .PLT file image based on it. This HP-GL/2 image may then be saved, rendered, and printed just like
any other .PLT file. A typical menu shortcut for the -A suffix analyzers looks like this:
instrument_0 HP 8566A / 8567A / 8568A (via HP-GL/2 emulation) at GPIB address 18\tF8
The normal host- or device-initiated plot menu options will not work with these instruments. If you use an older Prologix controller board, it will need to be upgraded to the version that supports software-selectable GPIB addressing.
The HP-GL/2 synthesis process takes place in less than a second, including the data acquisition itself. It's actually a great way to access the 8566B/8567B/8568B models as well; not only are 7470.EXE's synthesized HP-GL/2 plots much faster to acquire, but certain features such as markers look much better than they do in the B-series analyzers' own plots. Note, however, that a few features including the horizontal display-line cursor will not appear in a synthesized plot, nor will hardware diagnostic/error messages.
Device-Initiated Plots
If your instrument doesn't appear in the list above, that means it isn't directly supported by 7470.EXE, and won't work with the Acquire->Request functions, instrument menu shortcuts, or the command-line GPIB address feature. However, chances are good that you can still obtain plots from it by activating its front-panel "Plot" button while 7470.EXE is in the "Wait for device-initiated plot" mode. This mode may be selected from the Acquire menu, or by pressing the lower-case 'w' key.
GPIB Instrument and Interface Configuration Notes
Host-requested plotting requires 7470.EXE to carry on a two-way GPIB conversation with the instrument, so you'll need to configure your instrument for Talk/Listen mode (as opposed to Talk Only mode) for use with this feature. This typically involves changing a system-level menu option or DIP switch. All National Instruments GPIB adapters support host-requested plotting, but only versions 3.1 and later of the Prologix USB-GPIB adapter can provide the necessary GPIB-controller functionality. (For more information on the Prologix GPIB-USB board, you can email Prologix here.)
Device-initiated plotting usually requires the instrument to be configured for Talk-Only mode. When their front-panel PLOT buttons are pressed, some instruments, such as the HP analyzers, expect the plotter to be addressable at a specific GPIB address, usually 5. With National Instruments GPIB hardware, the emulated plotter address is controlled by 7470.EXE's GPIB menu; with a Prologix adapter in Device mode, the device address is a property of the DIP switch settings. Certain other instruments expect to be the only addressable instrument on the bus when their PLOT buttons are pressed, requiring selection of the "Listen only" option in 7470.EXE's GPIB menu, or address 0 on a Prologix board.
As you can imagine, experimentation is sometimes needed to find the right combination of device and host settings that will allow 7470.EXE to work with a particular instrument. Some notes on specific instruments appear below.
Pre-V1.5 instruments do a screen dump immediately after acquisition
7470 GPIB setting must be "No assigned plotter address (listen only)"
7470 GPIB setting must be "No assigned plotter address (listen only)"
Use Copy->HP_IBDefine->Talk Only, then set Plot_mode and do Copy Start
Also, if you have more than two or three powered-down instruments on the GPIB bus, keep in mind that they'll load the bus, possibly preventing successful communication with the instrument(s) that are turned on. When attempting to use 7470.EXE with a new instrument for the first time, it's best to use a simple direct connection between the instrument and the host PC's GPIB adapter.
I'm always interested in hearing from users of other instruments so they may be added to the list above. Please feel free to contact me at [email protected] with any bug reports or success stories.
Menu Commands and Keyboard Shortcuts
Key Menu Command Remarks
l File->Load HP-GL/2 data Retrieves a saved HP-GL/2 file (.PLT, .HPG, .PGL, .HGL) for viewing
s File->Save image or HP-GL/2 data Saves the currently-browsed plot as an HP-GL/2 file. Also can be
used to save the current window contents (which may consist of
several overlaid HP-GL/2 files) as a .GIF, .BMP, .TGA,
or .PCX image file
p File->Print image Sends the current window contents to the default Windows printer
Delete File->Close current plot Stop displaying/browsing the currently-visible plot. This command
does not delete the file; it simply removes it from
7470.EXE's current display list.
Ctrl-Delete File->Delete current plot file Same as File->Close current plot, except that it deletes the
HP-GL/2 file being viewed
Esc File->Quit
Space or F5 View->Refresh current display Reloads the currently-visible HP-GL/2 file. If the file was
acquired as a host-requested plot in the current 7470.EXE session,
it will be re-acquired.
b View->Browse sources one at a time Allows you to use the +/- keys to move through the list of
viewable plots, displaying them one at a time
o View->Overlay all sources Renders the graphical (i.e., non-text) portions of all loaded
or acquired HP-GL/2 plots atop each other. In Overlay mode,
the +/- keys are used to determine which plot contributes
text labels to the display.
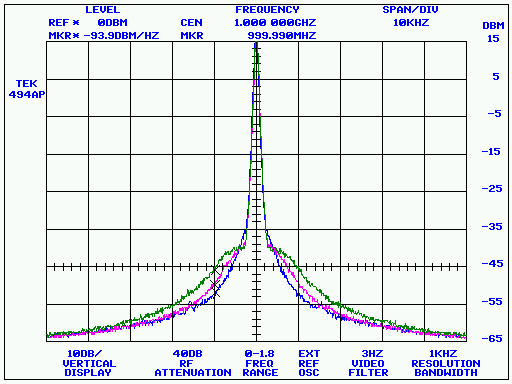
The three traces in the example image at the top of this page
were displayed with the View->Overlay command prior to being saved
as a .GIF file. (Use caution when closing or deleting a file in
Overlay mode. The visible text labels are the only way to tell
which file will be closed or deleted!)
+ View->Next source Navigates the list of visible HP-GL/2 plots. Specific behavior is
- View->Previous source determined by the choice of Browse/Overlay mode (above).
5 Display->512 x 384 Adjusts the size of 7470.EXE's window. Some crowded plots look much
Display->640 x 400 better at higher resolutions, but 7470.EXE will render an undersampled
6 Display->640 x 480 image if you you select a window size that's too large for the current
8 Display->800 x 600 Windows desktop. You can change the default window size in the 7470.INI
0 Display->1024 x 768 file (below.)
a Display->Aspect correction on Turn aspect correction on if Smith charts and other polar graphs appear
f Display->Aspect correction off squashed. Again, you can change the default setting in 7470.INI.
i Display->Alternate colors Useful for certain instruments such as the HP 8566/8568 analyzers
whose graticule and trace colors appear inverted in 7470.EXE.
(This option was added prior to the pen_colors array in 7470.INI,
which can be a better place to address color-rendering problems.)
w Acquire->Wait for device-initiated plot Enters a mode in which 7470.EXE waits for, and renders, HP-GL/2
data that arrives after pressing the front-panel PLOT button on an
instrument. You can press any key to exit this mode and restore
normal 7470.EXE operation.
W Acquire->Wait for device-initiated plot, Same as above, except that each incoming plot is sent to the
then print default Windows printer. If you set the auto_print_mode field in
7470.INI to '1', 7470.EXE will enter this mode on startup, acting
as an unattended HP-GL/2 print server.
Acquire->Request plot from supported When one of these options is selected, 7470.EXE will attempt to
device at GPIB address N(1-30) identify the instrument at the specified address and initiate a
host-requested plotting operation. This may entail sending
commands to the instrument to turn on its graticule display,
select HP-GL printing, and perform other setup tasks. Undefined
results may occur if the instrument does not appear in the list
under "Host-Requested Plots" above.
GPIB->No assigned plotter address During device-initiated plots, some instruments may need to
(listen-only) communicate with the (emulated) plotter, expecting to find it at a
specific GPIB address. Others may expect the plotter to be
GPIB->Plotter addressable at N(0-30) entirely transparent to the GPIB bus. If you are using a National
Instruments GPIB adapter, this menu allows you to specify the
plotter's address, or assign it no address at all.
When a Prologix GPIB-USB adapter is in use, this functionality
is provided by its DIP switch, and the GPIB menu will have no
effect.
7470.INI
The directory containing 7470.EXE should also contain a file called 7470.INI, which provides some configuration defaults that you can change if desired.
Most users won't need to edit this file. To configure the GPIB Toolkit for use with various versions of the Prologix GPIB adapter, you'll need to edit SERIAL.INI instead (see below).
Here is an example
of a 7470.INI file with comments explaining each line:
;
;Initial X/Y resolution
;
res_x 640
res_y 480
;
;Set to '1' if Smith charts and other polar graphs appear squashed
;
aspect_correction 0
;
;Set to '1' to display graphs in an alternate color set.
;Useful for the HP 8566B analyzer, possibly others
;
;'0' causes 7470 to use the default pen colors specified below
;
color_scheme 0
;
;Specify a higher value (in milliseconds) if 7470.EXE times
;out during device-initiated plotting
;
async_timeout 3500
;
;Options below are used to determine how the plotter responds to various
;output queries. No effect unless a valid GPIB board address is specified.
;Lines in this group may be commented out if necessary to suppress replies
;to a given query
;
OE_reply 0
OH_reply 0,0,10000,7500
OI_reply 7470A
OP_reply 0,0,10000,7500
OO_reply 0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0
OF_reply 40,40
;
;Set to '0' to suppress replies to OS (Output Status) command
;
process_OS 1
;
;Set to '1' to autodetect pen-storage commands in device-initiated plots,
;avoiding the need to wait for the async_timeout interval to expire at the
;end of each plot. Set to '0' if plots appear to be terminated prematurely
;
SP0_detect 1
;
;Sets the default plotter address in the GPIB menu. Use -1 for
;listen-only mode
;
default_board_addr 5
;
;For diagnostic/optimization purposes
;
async_xfer_size 100
async_GPIB_timeout 11
serial_read_timeout 500
release_sys_control 0
ignore_write_aborts 1
;
;Set to '1' to execute a 'W' (Acquire->Wait for device-initiated plot, then print)
;function automatically when 7470.EXE starts. Helpful if you want to make an
;unattended PC act as a dedicated HP-GL/2 print server
;
auto_print_mode 0
;
;Uncomment this line (remove the leading semicolon) to force
;7470.EXE to exit immediately after acquiring a plot and saving it.
;Normally, this line should be left commented out to run 7470 in its
;'interactive' mode. Note that if any command-line parameters are
;supplied when launching 7470, the auto_save_filename option is ignored
;
;auto_save_filename c:\my documents\automatic capture.gif
;
;Optional list of instrument/address pairs for the Acquire menu
;
;Entries should have the form 'instrument_n xxxx at GPIB address
GPIB Configuration and SERIAL.INI
The program directory should also contain a file called SERIAL.INI, which specifies the (real or virtual) RS-232 COM port settings for use with a serial GPIB adapter such as Prologix GPIB-USB boards.
To obtain host-requested plots with a Prologix adapter, the board must be configured for GPIB Controller mode, its address switches must match the instrument's GPIB address, and SERIAL.INI should be edited to set the controller_mode field to 1. To obtain device-initiated plots, it's usually a good idea to leave the Prologix board in Device mode with its DIP switches set to GPIB address 5. If you have an older Prologix board with no DIP switches, you will be limited to device-initiated plots. Either way, users of Prologix GPIB-USB and other serial adapters must edit SERIAL.INI to tell the GPIB Toolkit applications what COM port to use. See the comments in SERIAL.INI for more information.
If the COM port specification in SERIAL.INI is commented out with a leading semicolon - or if SERIAL.INI is missing entirely - all KE5FX GPIB Toolkit applications will attempt to use the National Instruments NI488.2 programming interface instead. This is the default configuration for most installations.
Note that some versions of Windows hide .INI file suffixes by default. In Windows 2000 and XP, for instance, SERIAL.INI may appear simply as "SERIAL," with the type "Configuration Settings." To turn off this behavior, go to the Tools->Folder Options->View tab in any Explorer window and deselect the "Hide file extensions for known file types" option.
Release Notes
Release 0.91 of 31-Oct-01
Acknowledgements and Additional Notes
My graphics library (WinVFX) doesn't support scalable/rotatable vector fonts. Consequently, text elements in plots will not appear exactly as they do when rendered by a LaserJet or HP-GL/2 plotter.
Thanks to Harrison Hooker, W8YMO for supplying information on the obsolete HP7470A command set.
Thanks to Vladan Temer of Sonoma Instrument Co. for supplying additional 7470A documentation and providing extensive assistance with support for various HP instruments in the 1.60 release.
If you find that 7470.EXE doesn't meet your needs, an excellent commercial alternative is PrintCapture. See the PrintCapture site for more information. Two more-expensive commercial packages from Aphena, which I haven't personally evaluated, are Plottergeist and SoftPlot.
Code compilable with any version of MSVC from VS6 to VS2005.NET, including the free Microsoft Visual Studio Express package
No warranties, expressed or implied, are offered with this program.
Use at your own risk!