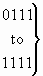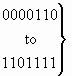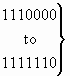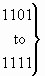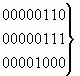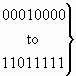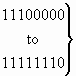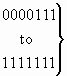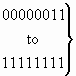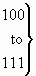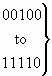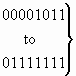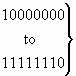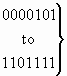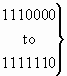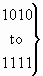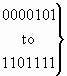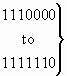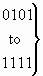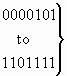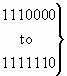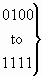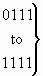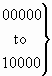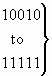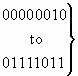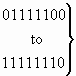3.2 Access delivery information
The format of the access delivery information parameter field is shown in Figure 4.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 4/Q.763 – Access delivery information parameter field
|
bit A:
|
Access delivery indicator
|
|
0
|
set-up message generated
|
|
1
|
no set-up message generated
|
| bits H-B: |
spare |
3.3 Access transport
The format of the access transport parameter field is shown in Figure 5.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
: |
|
: |
Information
element(s) |
: |
|
n |
|
Figure 5/Q.763 – Access transport parameter field
The information element is coded as described in 4.5/Q.931. Multiple Q.931 information
elements can be included within the access transport parameter. The information elements
applicable to a particular usage of the access transport parameter are dependent on, and
will be determined by, the relevant procedures. The maximum length of the access transport
parameter should only be limited by the message length as the content of the ATP will
probably evolve in the future.
3.4 Automatic congestion level
The format of the automatic congestion level parameter field is shown in Figure 6.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
Automatic congestion level |
Figure 6/Q.763 – Automatic congestion level parameter field
The following codes are used in the automatic congestion level parameter field:
3.5 Backward call indicators
The format of the backward call indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 7.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
2 |
P |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
Figure 7/Q.763 – Backward call indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the backward call indicators parameter field:
bits  : : |
Charge indicator (Note 1) |
| 0 0 |
no indication |
| 0 1 |
no charge |
| 1 0 |
charge |
| 1 1 |
spare |
| NOTE 1 – The interpretation of these bits
depends only on the charging exchange. |
|
|
bits 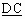 : : |
Called party's status indicator |
| 0 0 |
no indication |
| 0 1 |
subscriber free |
| 1 0 |
connect when free (national use) |
| 1 1 |
spare |
|
|
bits 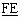 : : |
Called party's category
indicator |
| 0 0 |
no indication |
| 0 1 |
ordinary subscriber |
| 1 0 |
payphone |
| 1 1 |
spare |
|
|
bits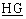 : : |
End-to-end method indicator (Note 2) |
| 0 0 |
no end-to-end method available (only
link-by-link method available) |
| 0 1 |
pass-along method available (national use) |
| 1 0 |
SCCP method available |
| 1 0 |
pass-along and SCCP methods available
(national use) |
|
|
| bit I: |
Interworking indicator
(Note 2) |
| 0 |
no interworking encountered
(Signalling System No. 7 all the way) |
| 1 |
interworking encountered |
|
|
| bit J: |
End-to-end information
indicator (national use) (Note 2) |
| 0 |
no end-to-end information
available |
| 1 |
end-to-end information available |
|
|
| bit K: |
ISDN user part indicator
(Note 2) |
| 0 |
ISDN user part not used all the
way |
| 1 |
ISDN user part used all the way |
|
|
| bit L: |
Holding indicator (national
use) |
| 0 |
holding not requested |
| 1 |
holding requested |
|
|
| bit M: |
ISDN access indicator |
| 0 |
terminating access non-ISDN |
| 1 |
terminating access ISDN |
|
|
| bit N: |
Echo control device indicator |
| 0 |
incoming echo control device not
included |
| 1 |
incoming echo control device
included |
|
|
bits 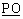 : : |
SCCP method indicator (Note 2) |
| 0 0 |
no indication |
| 0 1 |
connectionless method available (national use) |
| 1 0 |
connection oriented method available |
| 1 1 |
connectionless and connection oriented methods
available (national use) |
| NOTE 2 – Bits G-K and O-P constitute the
protocol control indicator. |
3.6 Call diversion information
The format of the call diversion information parameter field is shown in Figure 8.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 8/Q.763 – Call diversion information parameter field
The following codes are used in the call diversion information parameter field.
a) Notification subscription options
| bits CBA: |
|
| 0 0 0 |
Unknown |
| 0 0 1 |
presentation not allowed |
| 0 1 0 |
presentation allowed with redirection number |
| 0 1 1 |
presentation allowed without redirection
number |
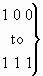
|
spare |
b) Redirecting reason
| bits GFED: |
|
| 0 0 0 0 |
Unknown |
| 0 0 0 1 |
User busy |
| 0 0 1 0 |
no reply |
| 0 0 1 1 |
unconditional |
| 0 1 0 0 |
deflection during alerting |
| 0 1 0 1 |
deflection immediate response |
| 0 1 1 0 |
mobile subscriber not reachable |
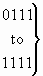
|
spare |
| bit H: |
spare |
3.7 Call history information
The format of the call history information parameter field is shown in Figure 42.
The call history information parameter expresses in pure binary representation the
propagation delay value of a call in ms.
3.8 Call reference (national use)
The format of the call reference parameter is shown in Figure 9.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
Call identity |
3 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
Signalling |
lsb |
5 |
spare |
msb point code |
Figure 9/Q.763 – Call reference parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the call reference parameter field:
a) Call identity
A code expressing in pure binary representation the identification number allocated
to the call.
b) Signalling point code
The code of the signalling point in which the call identity is relevant.
3.9 Called party number
The format of the called party number parameter field is shown in Figure 10.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
2 |
INN |
Numbering plan
indicator |
spare |
3 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
:
: |
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 10/Q.763 – Called party number parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the called party number parameter
field:
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E)
0 even number of address signals
1 odd number of address signals
b) Nature of address indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
network-specific number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 |
network routeing number in national (significant) number
format (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 |
network routeing number in network-specific number format
(national use) |
| 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 |
network routeing number concatenated with Called Directory
Number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 ü
to ý
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 þ |
spare |
| 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ü
to ý
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 þ |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
c) Internal Network Number indicator (INN)
0 routeing to internal network number allowed
1 routeing to internal network number not allowed
d) Numbering plan indicator
0 0 0 spare
0 0 1 ISDN (Telephony) numbering plan (Recommendation E.164)
0 1 0 spare
0 1 1 Data numbering plan (Recommendation X.121) (national use)
1 0 0 Telex numbering plan (Recommendation F.69) (national use)
1 0 1 reserved for national use
1 1 0 reserved for national use
1 1 1 spare
e) Address signal
0 0 0 0 digit 0
0 0 0 1 digit 1
0 0 1 0 digit 2
0 0 1 1 digit 3
0 1 0 0 digit 4
0 1 0 1 digit 5
0 1 1 0 digit 6
0 1 1 1 digit 7
1 0 0 0 digit 8
1 0 0 1 digit 9
1 0 1 0 spare
1 0 1 1 code 11
1 1 0 0 code 12
1 1 0 1 spare
1 1 1 0 spare
1 1 1 1 ST
The most significant address signal is sent first. Subsequent address signals are sent
in successive 4-bit fields.
f) Filler
In case of an odd number of address signals, the filler code 0000 is inserted after
the last address signal.
3.10 Calling party number
The format of the calling party number parameter field is shown in Figure 11.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
2 |
NI |
Numbering plan
indicator |
Address
presentation restricted indicator |
Screening
indicator |
3 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
:
: |
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 11/Q.763 – Calling party number parameter field
The following codes are used in the calling party number parameter field.
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a)
b) Nature of address indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
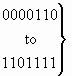 |
spare |
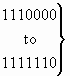 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
c) Number Incomplete indicator (NI)
0 complete
1 incomplete
d) Numbering plan indicator: as Subclause 3.9 d)
e) Address presentation restricted indicator
0 0 presentation allowed
0 1 presentation restricted
1 0 address not available (Note) (national use)
1 1 reserved for restriction by the network
NOTE – If the parameter is included and the address presentation
restricted indicator indicates address not available, octets 3 to n are omitted, the
subfields in items a), b), c) and d) are coded with 0's, and the subfield f) is coded with
11.
f) Screening indicator
0 0 reserved (Note)
0 1 user provided, verified and passed
1 0 reserved (Note)
1 1 network provided
NOTE – Code 00 and 10 are reserved for "user provided, not
verified" and "user provided, verified and failed" respectively. Codes 00
and 10 are for national use.
g) Address signal
| 0 0 0 0 |
digit 0 |
| 0 0 0 1 |
digit 1 |
| 0 0 1 0 |
digit 2 |
| 0 0 1 1 |
digit 3 |
| 0 1 0 0 |
digit 4 |
| 0 1 0 1 |
digit 5 |
| 0 1 1 0 |
digit 6 |
| 0 1 1 1 |
digit 7 |
| 1 0 0 0 |
digit 8 |
| 1 0 0 1 |
digit 9 |
| 1 0 1 0 |
spare |
| 1 0 1 1 |
code 11 |
| 1 1 0 0 |
code 12 |
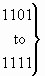 |
spare |
h) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.11 Calling party's category
The format of the calling party's category parameter field is shown in Figure 12.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
Calling party's category |
Figure 12/Q.763 – Calling party's category parameter field
The following codes are used in the calling party's category parameter field.
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
calling party's category unknown at this time
(national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
operator, language French |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
operator, language English |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
operator, language German |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
operator, language Russian |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
operator, language Spanish |
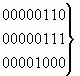 |
(available to Administrations for selection
a particular language
by mutual agreement) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 |
reserved (see Recommendation Q.104) (Note)
(national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 |
ordinary calling subscriber |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 |
calling subscriber with priority |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 |
data call (voice band data) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 |
test call |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 |
payphone |
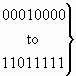 |
spare |
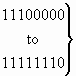 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
| NOTE – In national networks, code
00001001 may be used to indicate that the calling party is a national operator. |
3.12 Cause indicators
The format of the cause indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 13.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
ext. |
Coding standard |
spare |
Location |
2 |
ext. |
Cause value |
3
:
:
3n |
Diagnostic(s) (if any) |
| |
NOTE - Octets 3 to 3n may be
omitted or repeated, e.g. 3’ to 3n’. |
Figure 13/Q.763 – Cause indicators parameter field
The codes to be used in the subfields of the cause indicators parameter fields are
defined in Recommendation Q.850.
3.13 Circuit group supervision message type
The format of the circuit group supervision message type parameter field is shown in
Figure 14.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 14/Q.763 – Circuit group supervision message type parameter
field
The following codes are used in the circuit group supervision message type parameter
field:
bits BA: Circuit group supervision message type indicator
0 0 maintenance oriented
0 1 hardware failure oriented
1 0 reserved for national use (used in 1984 version)
1 1 spare
bits H-C: spare
3.14 Circuit state indicator (national use)
The format of the circuit state indicator parameter field is shown in Figure 15.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 15/Q.763 – Circuit state indicator parameter field
The number of octets in the circuit state indicator parameter field is equal to the
specified range + 1. Each circuit state indicator octet is associated with a
circuit identification code such that octet n is associated with circuit identification
code m + n - 1, where m is the circuit
identification code contained in the message.
The following codes are used in each circuit state indicator octet:
a) for bits D C = 00
bits BA: Maintenance blocking state
0 0 transient
0 1 spare
1 0 spare
1 1 unequipped
bits H-E: spare
b) for bits D C not equal to 00
bits BA: Maintenance blocking state
0 0 no blocking (active)
0 1 locally blocked
1 0 remotely blocked
1 1 locally and remotely blocked
bits DC: Call processing state
0 1 circuit incoming busy
1 0 circuit outgoing busy
1 1 idle
bits F E: Hardware blocking state (Note)
0 0 no blocking (active)
0 1 locally blocked
1 0 remotely blocked
1 1 locally and remotely blocked
bits H-G: spare
NOTE – If bits F E are not coded 0 0, bits D C must be coded 1 1.
3.15 Closed user group interlock code
The format of the closed user group interlock code parameter field is shown in
Figure 16.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1st NI digit |
2nd NI digit |
2 |
3rd NI digit |
4th NI digit |
3 |
msb |
|
|
4 |
|
Binary code |
lsb |
Figure 16/Q.763 – Closed user group interlock code parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the closed user group interlock code
parameter field:
a) Network Identity (NI) (octets 1 and 2)
Each digit is coded in the binary coded decimal representation from 0 to 9. If the
first digit of this field is coded 0 or 9, the TCC (Telephony Country Code) follows in the
second to fourth NI digits (the most significant TCC digit is in the 2nd NI digit). If the
TCC is one or two digits long, the excess digit(s) is inserted with the code for RPOA or
network identification, if necessary. If octet 2 is not required, it is coded all zeros.
Coding of the first digit as 1 or 8 is excluded.
If the first digit is not 0, 9, 1 or 8, this field contains a DNIC (Data Network
Identification Code) as defined in Recommendation X.121.
b) Binary code (octets 3 and 4)
A code allocated to a closed user group administered by a particular ISDN or data
network. Bit 8 of octet 3 is the most significant and bit 1 of octet 4 is the least
significant.
3.16 Connected number
The format of the connected number parameter field is shown in Figure 17.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
2 |
spare |
Numbering plan
indicator |
Address
presentation restricted indicator |
Screening
indicator |
3 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
:
: |
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 17/Q.763 – Connected number parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the connected number parameter field:
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a).
b) Nature of address indicator: as Subclause 3.10 b).
c) Numbering plan indicator: as Subclause 3.9 d).
d) Address presentation restricted indicator:
0 0 presentation allowed
0 1 presentation restricted
1 0 address not available
1 1 spare
NOTE – If the parameter is included and the address presentation
restricted indicator indicates address not available, octets 3 to n are omitted, the
subfields in items a), b), and c) are coded with 0's, and the screening indicator is set
to 11 network provided.
e) Screening indicator: as Subclause 3.10 f).
f) Address signal: as Subclause 3.10 g).
g) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.17 Connection request
The format of the connection request parameter field is shown in Figure 18.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
Local reference |
3 |
|
4 |
Signalling point
lsb |
5 |
spare |
msb code |
6 |
Protocol class |
7 |
Credit |
| |
NOTE - Octets 6 and 7 may be
omitted if protocol class requested is 2. |
Figure 18/Q.763 – Connection request parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the connection request parameter
field:
a) Local reference
A code indicating the local reference allocated by the signalling connection
control part to the end-to-end connection.
b) Signalling point code
A code identifying the signalling point at which the connection request originated.
c) Protocol class
A code identifying in pure binary representation, the protocol class requested for
the end-to-end connection.
d) Credit
A code identifying in pure binary representation the window size requested for the
end-to-end connection.
3.18 Continuity indicators
The format of the continuity indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 19.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 19/Q.763 – Continuity indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the continuity indicators parameter field:
bit A: Continuity indicator
0 continuity check failed
1 continuity check successful
bits H-B spare
3.19 Echo control information
The format of the echo control information parameter field is shown in Figure 20.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 20/Q.763 – Echo control information parameter field
a) bits BA: Outgoing echo control device information indicator
0 0 no information
0 1 outgoing echo control device not included and not available
1 0 outgoing echo control device included
1 1 outgoing echo control device not included but available
b) bits DC: Incoming echo control device information indicator
0 0 no information
0 1 incoming echo control device not included and not available
1 0 incoming echo control device included
1 1 incoming echo control device not included but available
c) bits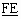 : Outgoing echo control device request indicator
: Outgoing echo control device request indicator
0 0 no information
0 1 outgoing echo control device activation request
1 0 outgoing echo control device deactivation request (Note)
1 1 spare
NOTE – This value will not be generated by the Echo
Control Logic defined in Recommendation Q.115.
d) bits HG: Incoming echo control device request indicator
0 0 no information
0 1 incoming echo control device activation request
1 0 incoming echo control device deactivation request (Note)
1 1 spare
NOTE – This value will not be generated by the Echo
Control Logic defined in Recommendation Q.115.
3.20 End of optional parameters
The last optional parameter field of a message is followed by the end of optional
parameters octet (see Subclause 1.8).
3.21 Event information
The format of the event information parameter field is shown in Figure 21.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 21/Q.763 – Event information parameter field
The following codes are used in the event indicator parameter field:
|
|
bits 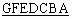 : : |
Event indicator |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
ALERTING |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
PROGRESS |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
in-band information or an appropriate pattern is now
available |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
call forwarded on busy (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
call forwarded on no reply (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 |
call forwarded unconditional (national use) |
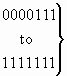 |
spare (Note) |
| NOTE – Coding of this indicator is
frozen; no additional codes can be defined for compatibility. |
|
|
| bit H: |
Event presentation restricted indicator (national use) |
| 0 |
no indication |
| 1 |
presentation restricted |
3.22 Facility indicator
The format of the facility indicator parameter field is shown in Figure 22.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
Facility indicators |
Figure 22/Q.763 – Facility indicator parameter field
The following codes are used in the facility indicator parameter field:
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
user-to-user service |
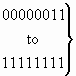 |
spare |
3.23 Forward call indicators
The format of the forward call indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 23.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
2 |
P |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
Figure 23/Q.763 – Forward call indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the forward call indicators parameter field:
bit A: National/international call indicator (Note 1)
0 call to be treated as a national call
1 call to be treated as an international call
bits CB: End-to-end method indicator (Note 2)
0 0 no end-to-end method available (only link-by-link method available)
0 1 pass-along method available (national use)
1 0 SCCP method available
1 1 pass-along and SCCP methods available (national use)
bit D: Interworking indicator (Note 2)
0 no interworking encountered (No. 7 signalling all the way)
1 interworking encountered
bit E: End-to-end information indicator (national use) (Note 2)
0 no end-to-end information available
1 end-to-end information available
bit F: ISDN user part indicator (Note 2)
0 ISDN user part not used all the way
1 ISDN user part used all the way
bits HG: ISDN user part preference indicator
0 0 ISDN user part preferred all the way
0 1 ISDN user part not required all the way
1 0 ISDN user part required all the way
1 1 spare
bit I: ISDN access indicator
0 originating access non-ISDN
1 originating access ISDN
bits KJ: SCCP method indicator (Note 2)
0 0 no indication
0 1 connectionless method available (national use)
1 0 connection oriented method available
1 1 connectionless and connection oriented methods available (national use)
bit L: spare
bits P-M: reserved for national use
NOTE 1 – Bit A can be set to any value in the country of origin. In the
international network this bit is not checked. In the destination country, calls from the
international network will have this bit set to 1.
NOTE 2 – Bits B-F and J-K constitute the protocol control indicator.
3.24 Generic digits (national use)
The format of the generic digits parameter field is shown in Figure 24.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
Encoding scheme |
Type of digits |
2 |
digits |
: |
|
: |
|
: |
|
n |
digits |
Figure 24/Q.763 – Generic digits parameter
The following codes are used in the subfields of the generic digits parameter:
a) Encoding scheme
| 0 0 0 |
BCD even: (even number of digits) |
| 0 0 1 |
BCD odd: (odd number of digits) |
| 0 1 0 |
IA5 character |
| 0 1 1 |
binary coded |
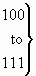 |
spare |
b) Type of digits
| 0 0 0 0 0 |
reserved for account code |
| 0 0 0 0 1 |
reserved for authorisation code |
| 0 0 0 1 0 |
reserved for private networking travelling class mark |
| 0 0 0 1 1 |
reserved for business communication group identity |
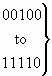 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 |
reserved for extension |
c) Digit
Coding in accordance to the coding scheme and type of digits.
3.25 Generic notification indicator
The format of the generic notification indicator parameter field is shown in
Figure 25.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
ext. |
Notification
indicator |
Figure 25/Q.763 – Generic notification indicator parameter field
The following codes are used in the generic notification indicator parameter field:
a) Extension indicator (ext.)
0 information continues in the next octet
1 last octet
b) Notification indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
user suspended |
|
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
user resumed |
|
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
bearer service change
discriminator for extension to ASN.1
encoded component |
 |
(used in DSS 1) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
call completion delay |
|
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 to
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
) ) reserved
) |
|
| 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
conference established |
|
| 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
conference disconnected |
|
| 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
other party added |
|
| 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
isolated |
|
| 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 |
reattached |
|
| 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 |
other party isolated |
|
| 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 |
other party reattached |
|
| 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 |
other party split |
|
| 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 |
other party disconnected |
|
| 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 |
conference floating |
|
| 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 to
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 |
) ) reserved
) |
|
| 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 |
call is a waiting call |
|
| 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 to
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 |
) ) reserved
) |
|
| 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 |
diversion activated (used in DSS 1) |
|
| 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 |
call transfer, alerting |
|
| 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 |
call transfer, active |
|
| 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 to
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 |
) ) reserved
) |
|
| 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 |
remote hold |
|
| 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 |
remote retrieval |
|
| 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 |
call is diverting |
|
| 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 to
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
) ) reserved
) |
|
3.26 Generic number
The format of the generic number parameter field is shown in Figure 26.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
Number qualifier
indicator |
2 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
3 |
NI |
Numbering plan
indicator |
Address
presentation restricted indicator |
Screening
indicator |
4 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 26/Q.763 – Generic number parameter field
The following codes are used in the generic number parameter field:
a) Number qualifier indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
reserved (dialled digits) (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
additional called number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
reserved (supplemental user provided calling number –
failed network screening) (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
reserved (supplemental user provided calling
number – not screened) (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
reserved (redirecting terminating number) (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
additional connected number |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 |
additional calling party number |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 |
reserved for additional original called number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 |
reserved for additional redirecting number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 |
reserved for additional redirection number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 |
reserved (used in 1992 version) |
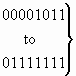 |
spare |
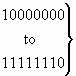 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
reserved for expansion |
b) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a)
c) Nature of address indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
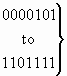 |
spare |
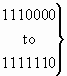 |
reserved for national use |
|
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
|
spare
|
NOTE – For each supplementary service the relevant codes and
possible default settings are described in the supplementary service Recommendations
(Recommendation Q.73x).
d) Number incomplete indicator (NI)
0 number complete
1 number incomplete
e) Numbering plan indicator
0 0 0 spare
0 0 1 ISDN (telephony) numbering plan (Recommendation E.164)
0 1 0 spare
0 1 1 data numbering plan (Recommendation X.121) (national use)
1 0 0 telex numbering plan (Recommendation F.69) (national use)
1 0 1 private numbering plan (national use)
1 1 0 reserved for national use
1 1 1 spare
NOTE – For each supplementary service the relevant codes and
possible default settings are described in the supplementary service Recommendations
(Recommendation Q.73x).
f) Address presentation restricted indicator
0 0 presentation allowed
0 1 presentation restricted
1 0 address not available
1 1 spare
NOTE – For each supplementary service the relevant codes and
possible default settings are described in the supplementary service Recommendations
(Recommendation Q.73x). When the address presentation restricted indicator indicates
address not available, the subfields in items b), c), d), and e) are coded with 0's, and
the screening indicator is set to 11 (network provided).
g) Screening indicator
Only used if the number qualifier indicator is coded 0000 0101 (additional
connected number) or 0000 0110 (additional calling party number). This indicator is coded
as follows:
0 0 user provided, not verified
0 1 user provided, verified and passed
1 0 user provided, verified and failed
1 1 network provided
NOTE – For each supplementary service the relevant codes and
possible default settings are described in the supplementary service Recommendations
(Recommendation Q.73x).
h) Address signal:
| 0 0 0 0 |
digit 0 |
| 0 0 0 1 |
digit 1 |
| 0 0 1 0 |
digit 2 |
| 0 0 1 1 |
digit 3 |
| 0 1 0 0 |
digit 4 |
| 0 1 0 1 |
digit 5 |
| 0 1 1 0 |
digit 6 |
| 0 1 1 1 |
digit 7 |
| 1 0 0 0 |
digit 8 |
| 1 0 0 1 |
digit 9 |
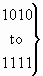 |
spare |
i) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f)
3.27 Reserved (used in 1992 version)
3.28 Information indicators (national use)
The format of the information indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 28.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
2 |
P |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
Figure 28/Q.763 – Information indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the information indicators parameter field:
bits BA: Calling party address response indicator
0 0 calling party address not included
0 1 calling party address not available
1 0 spare
1 1 calling party address included
bit C: Hold provided indicator
0 hold not provided
1 hold provided
bits ED: spare
bit F: Calling party's category response indicator
0 calling party's category not included
1 calling party's category included
bit G: Charge information response indicator
0 charge information not included
1 charge information included
bit H: Solicited information indicator
0 solicited
1 unsolicited
bits L-I: spare
bits P-M: reserved
3.29 Information request indicators (national use)
The format of the information request indicators parameter field is shown in
Figure 29.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
2 |
P |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
Figure 29/Q.763 – Information request indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the information request indicators parameter field:
bit A: Calling party address request indicator
0 calling party address not requested
1 calling party address requested
bit B: Holding indicator
0 holding not requested
1 holding requested
bit C: spare
bit D: Calling party's category request indicator
0 calling party's category not requested
1 calling party's category requested
bit E: Charge information request indicator
0 charge information not requested
1 charge information requested
bits GF: spare
bit H: Malicious call identification request indicator (reserved, used in
ISUP'88 Blue Book)
0 malicious call identification not requested
1 malicious call identification requested
bits L-I: spare
bits P-M: reserved
3.30 Location number
The format of the location number field is shown in Figure 30.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
2 |
INN |
Numbering plan
indicator |
Address
presentation restricted indicator |
Screening
indicator |
3 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
:
: |
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 30/Q.763 – Location number parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the location number parameter field:
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a).
b) Nature of address indicator
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
reserved for subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
reserved for unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
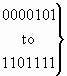 |
spare |
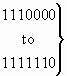 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
c) Internal Network Number indicator (INN)
0 routeing to internal number allowed
1 routeing to internal number not allowed
d) Numbering plan indicator
0 0 0 spare
0 0 1 ISDN (telephony) numbering plan (Recommendation E.164)
0 1 0 spare
0 1 1 Data numbering plan (Recommendation X.121) (national use)
1 0 0 Telex numbering plan (Recommendation F.69) (national use)
1 0 1 private numbering plan
1 1 0 reserved for national use
1 1 1 spare
e) Address presentation restricted indicator
0 0 presentation allowed
0 1 presentation restricted
1 0 address not available (national use)
1 1 spare
NOTE – When the address presentation restricted indicator indicates
address not available, the subfields in items a), b), c) and d) are coded with 0's, and
the screening indicator is set to 11 (network provided).
f) Screening indicator
0 0 reserved
0 1 user provided, verified and passed
1 0 reserved
1 1 network provided
g) Address signals: as Subclause 3.26 h).
h) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.31 MCID request indicators
The format of the MCID request indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 31.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 31/Q.763 – MCID request indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the MCID request indicators parameter field:
bit A: MCID request indicator
0 MCID not requested
1 MCID requested
bit B: Holding indicator (national use)
0 holding not requested
1 holding requested
bits H-C: spare
3.32 MCID response indicators
The format of the MCID response indicators parameter field is shown in Figure 32.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 32/Q.763 – MCID response indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the MCID response indicators parameter field:
bit A: MCID response indicator
0 MCID not included
1 MCID included
bit B: Hold provided indicator (national use)
0 holding not provided
1 holding provided
bits H-C: spare
3.33 Message compatibility information
The format of the message compatibility information parameter field is shown in
Figure 33.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
| |
Instruction
indicator |
Figure 33/Q.763 – Message compatibility information parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the message compatibility information
parameter field:
a) Instruction indicators
The format of the instruction indicators subfield is shown Figure 34.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
ext. |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
1a |
ext. |
More instruction
indicators if required |
:
: |
:
: |
1n |
1 |
More instruction
indicators if required |
Figure 34/Q.763 – Instruction indicators subfield
The following codes are used in the instructions indicators subfield:
bit A: Transit at intermediate exchange indicator
0 transit interpretation
1 end node interpretation
bit B: Release call indicator
0 do not release call
1 release call
bit C: Send notification indicator
0 do not send notification
1 send notification
bit D: Discard message indicator
0 do not discard message (pass on)
1 discard message
bit E: Pass on not possible indicator
0 release call
1 discard information
bits G F: Broadband/narrowband interworking indicator
0 0 pass on
0 1 discard message
1 0 release call
1 1 reserved, assume 00
b) Extension indicator (ext.): as Subclause 3.25 a).
c) More instruction indicators
The bits will be defined when required.
3.34 MLPP precedence
The format of the MLPP precedence parameter field is shown in Figure 35.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
spare |
LFB |
spare |
Precedence level |
2 |
1st NI digit |
2nd NI digit |
3 |
3rd NI digit |
4th NI digit |
4 |
|
5 |
MLPP service
domain |
6 |
|
Figure 35/Q.763 – MLPP precedence parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the MLPP precedence parameter field:
a) LFB (Look ahead for busy)
| 0 0 |
LFB allowed |
| 0 1 |
path reserved (national use) |
| 1 0 |
LFB not allowed |
| 1 1 |
spare |
b) Precedence level
| 0 0 0 0 |
flash override |
| 0 0 0 1 |
flash |
| 0 0 1 0 |
immediate |
| 0 0 1 1 |
priority |
| 0 1 0 0 |
routine |
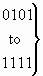 |
spare |
c) Network Identity (NI) octet 2 and 3
Each digit is coded in binary coded decimal representation from 0 to 9.
The first digit of this field is coded 0. The TCC (Telephony Country Code) follows in
the second to fourth NI digits (the most significant TCC digit is in the 2nd NI digit). If
the TCC is one or two digits long, the excess digit(s) is inserted with the code for ROA
or network identification, if necessary. If octet 3 is not required, it is coded all
zeros.
d) MLPP service domain (octet 4, 5 and 6)
A code pure binary coded allocated to a MLPP service domain administered by a
particular ISDN. Bit 8 of octet 4 is the most significant and bit 1 of octet 6 is the
least significant respectively.
3.35 Nature of connection indicators
The format of the nature of connection indicators parameter field is shown in
Figure 36.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 36/Q.763 – Nature of connection indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the nature of connection indicators parameter field:
bits BA: Satellite indicator
0 0 no satellite circuit in the connection
0 1 one satellite circuit in the connection
1 0 two satellite circuits in the connection
1 1 spare
bits DC: Continuity check indicator
0 0 continuity check not required
0 1 continuity check required on this circuit
1 0 continuity check performed on a previous circuit
1 1 spare
bit E: Echo control device indicator
0 outgoing echo control device not included
1 outgoing echo control device included
bits H-F: spare
3.36 Network specific facility (national use)
The format of the network specific facility parameter field is shown in Figure 37.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
Length of
network identification |
1a |
ext. |
Type of network
identification |
Network
identification plan |
1b |
|
|
: |
spare |
Network
identification |
: |
|
|
1m |
0 |
|
2 |
|
: |
Network specific
facility indicator |
n |
|
Figure 37/Q.763 – Network specific facility parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the network specific facility
parameter field:
a) Length of network identification
This field contains the length, in octets, of the network identification found in
octets 1a, 1b-1m. If the value is 0000 0000, then octets 1a-1m are omitted.
b) Extension (ext.): as Subclause 3.25 a).
c) Type of network identification
The following codes are used in the type of network identification subfield:
0 1 0 national network identification
0 1 1 reserved for international network identification (Note)
100 )
to ) spare
111 )
When the type of network identification is coded 010 "national network
identification", the network identification plan, and network identification is coded
nationally.
NOTE – The value 011 is reserved for international use, in case the
parameter will be accepted for international use in the future.
d) Network identification plan
e) Network identification
f) Network-specific facility indicator
This field is encoded according to the rules specified by the identified network.
The network may specify the same coding rule as stimulus type of information elements in
Recommendation Q.932. In this case multiple information elements may be included in this
field.
3.37 Optional backward call indicators
The format and codes of the optional backward call indicators field is shown in
Figure 38.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 38/Q.763 – Optional backward call indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the optional backward call indicators parameter field:
bit A: In-band information indicator
0 no indication
1 in-band information or an appropriate pattern is now available
bit B: Call diversion may occur indicator
0 no indication
1 call diversion may occur
bit C: Simple segmentation indicator
0 no additional information will be sent
1 additional information will be sent in a segmentation message
bit D: MLPP user indicator
0 no indication
1 MLPP user
bits H-E: reserved for national use
3.38 Optional forward call indicators
The format of the optional forward call indicators parameter field is shown in
Figure 39.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 39/Q.763 – Optional forward call indicators parameter field
The following codes are used in the optional forward call indicators parameter field:
bits BA: Closed user group call indicator
0 0 non-CUG call
0 1 spare
1 0 closed user group call, outgoing access allowed
1 1 closed user group call, outgoing access not allowed
bit C: Simple segmentation indicator
0 no additional information will be sent
1 additional information will be sent in a segmentation message
bits G-D: spare
bit H: Connected line identity request indicator
0 not requested
1 requested
3.39 Original called number
The format of the original called number parameter field is shown in Figure 40.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
O/E |
Nature of
address indicator |
2 |
spare |
Numbering plan
indicator |
Address
presentation restricted indicator |
spare |
3 |
2nd address
signal |
1st address
signal |
:
: |
|
|
m |
Filler (if
necessary) |
nth
address signal |
Figure 40/Q.763 – Original called number parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the original called number parameter
field:
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a).
b) Nature of address indicator:
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
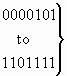 |
spare |
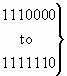 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
c) Numbering plan indicator: as Subclause 3.9 d).
d) Address presentation restricted indicator: as Subclause 3.10 e).
e) Address signal: as Subclause 3.10 g).
f) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.40 Origination ISC point code
The format of the origination ISC point code parameter field is shown in
Figure 50.
3.41 Parameter compatibility information
The format of the parameter compatibility information parameter field is shown in
Figure 41.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1st upgraded
parameter |
2 |
Instruction
indicators |
: |
|
: |
|
2n-1 |
nth
upgraded parameter |
2n |
Instruction
indicators |
Figure 41/Q.763 – Parameter compatibility information parameter
field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the parameter compatibility
information parameter field:
a) Nth upgraded parameter name
This field contains the parameter name of the nth upgraded parameter in
accordance with Table 5.
b) Instruction indicators
The format of the instruction indicators subfield is shown in Figure 41.1.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
ext. |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
1a |
ext. |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
:
: |
|
|
|
|
: : |
|
|
|
1n |
|
More instruction
indicators if required |
Figure 41.1/Q.763 – Instruction indicators subfield
The following codes are used in the instructions indicators subfield:
bit A: Transit at intermediate exchange indicator
0 transit interpretation
1 end node interpretation
bit B: Release call indicator
0 do not release call
1 release call
bit C: Send notification indicator
0 do not send notification
1 send notification
bit D: Discard message indicator
0 do not discard message (pass on)
1 discard message
bit E: Discard parameter indicator
0 do not discard parameter (pass on)
1 discard parameter
bits G F: Pass on not possible indicator
0 0 release call
0 1 discard message
1 0 discard parameter
1 1 reserved (interpreted as 00)
c) Extension indicator (ext.): as Subclause 3.25 a).
d) bits J I: Broadband/narrowband interworking indicator
0 0 pass on
0 1 discard message
1 0 release call
1 1 discard parameter
e) bits O-K: spare
f) More instruction indicators
The bits will be defined when required.
3.42 Propagation delay counter
The format of the propagation delay counter parameter field is shown in Figure 42.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
msb |
Propagation |
2 |
delay value |
lsb |
Figure 42/Q.763 – Propagation delay counter parameter field
The propagation delay counter parameter expresses in pure binary representation the
propagation delay value of a call in ms to be accumulated during call set-up.
3.43 Range and status
The format of the range and status parameter field is shown in Figure 43.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
Range |
2
:
:
:
n |
Status |
Figure 43/Q.763 – Range and status parameter field
The following codes are used in the subfields of the range and status parameter field:
a) Range
A number in pure binary representation ranging from 0 to 255. The number
represented by the range code + 1 indicates the range of circuits affected by the message.
The number of circuits affected by a group supervision message is limited to 32 or
less. For the group reset messages, a circuit group query message, or a circuit query
response message, this requires that the range value be 31 or less. For the group blocking
and unblocking messages the range value may be up to 255, but the number of status bits
set to 1 must be 32 or less.
For the group blocking, unblocking and reset messages, range code 0 is reserved. Range
code 0 is exclusively used by the circuit query and circuit query response messages.
b) Status
The status subfield contains from 2 to 256 status bits numbered from 0 to 255.
Status bit 0 is located in bit position 1 of the first status subfield octet. Other status
bits follow in numerical order. The number of relevant status bits in a given status
subfield is equal to range + 1.
Each status bit is associated with a circuit identification code such that status bit n
is associated with circuit identification code m + n, where m is the circuit
identification code contained in the message.
The status bits are coded as follows:
– in circuit group blocking messages
0 no indication
1 blocking
– in circuit group blocking acknowledgement messages
0 no indication
1 blocking acknowledgement
– in circuit group unblocking messages
0 no indication
1 unblocking
– in circuit group unblocking acknowledgement messages
0 no indication
1 unblocking acknowledgement
– in circuit group reset acknowledgement messages
0 not blocked for maintenance reasons
1 blocked for maintenance reasons
3.44 Redirecting number
The format of the redirecting number parameter field is shown in Figure 40.
The following codes are used in the subfields of the redirecting number parameter
field:
a) Odd/even indicator: as Subclause 3.9 a)
b) Nature of address indicator: as Subclause 3.10 b)
c) Numbering plan indicator: as Subclause 3.9 d)
d) Address presentation restricted indicator: as Subclause 3.10 e)
e) Address signal: as Subclause 3.10 g)
f) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.45 Redirection information
The format of the redirection information parameter field is shown in Figure 44.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
2 |
P |
O |
N |
M |
L |
K |
J |
I |
| NOTE – The parameter may be received
without the second octet from an ISUP'88 (Blue Book). |
Figure 44/Q.763 – Redirection information parameter field
The following codes are used in the redirection information parameter field:
| bits CBA: |
Redirecting indicator |
| 0 0 0 |
no redirection (national use) |
| 0 0 1 |
call rerouted (national use) |
| 0 1 0 |
call rerouted, all redirection information
presentation restricted (national use) |
| 0 1 1 |
call diverted |
| 1 0 0 |
call diverted, all redirection information
presentation restricted |
| 1 0 1 |
call rerouted, redirection number presentation
restricted (national use) |
| 1 1 0 |
call diversion, redirection number
presentation restricted (national use) |
| 1 1 1 |
spare |
| bit D: |
spare |
|
|
| bits HGFE: |
Original redirection reason |
| 0 0 0 0 |
unknown/not available |
| 0 0 0 1 |
user busy (national use) |
| 0 0 1 0 |
no reply (national use) |
| 0 0 1 1 |
unconditional (national use) |
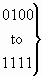 |
spare |
|
|
| bits K J I: |
Redirection counter Number of
redirections the call has undergone expressed as a binary number between 1 and 5. |
| bit L: |
reserved for national use |
|
|
| bits PONM: |
Redirecting reason |
| 0 0 0 0 |
unknown/not available |
| 0 0 0 1 |
user busy |
| 0 0 1 0 |
no reply |
| 0 0 1 1 |
unconditional |
| 0 1 0 0 |
deflection during alerting |
| 0 1 0 1 |
deflection immediate response |
| 0 1 1 0 |
mobile subscriber not reachable |
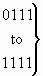 |
spare |
3.46 Redirection number
The format of the redirection number parameter field isis shown in Figure 10.
The following codes are used in the subfields of the redirection number parameter
field:
a) Odd/even indicator (O/E): as Subclause 3.9 a).
b) Nature of address indicator:
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
subscriber number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 |
unknown (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 |
national (significant) number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 |
international number |
| 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 |
network routeing number in national (significant) number
format (national use) |
| 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 |
network routeing number in network-specific number format
(national use) |
| 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 |
reserved for network routeing number concatenated with Called
Directory Number (national use) |
| 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 ü
to ý
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 þ |
spare |
| 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ü
to ý
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 þ |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
spare |
c) Internal network number indicator (INN): as Subclause 3.9 c).
d) Numbering plan indicator: as Subclause 3.9 d).
e) Address signal: as Subclause 3.10 g).
f) Filler: as Subclause 3.9 f).
3.47 Redirection number restriction
The format of the redirection number presentation parameter field is shown in
Figure 45.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Figure 45/Q.763 – Redirection number restriction parameter field
The following codes are used in the redirection number restriction parameter field:
bits BA: Presentation restricted indicator
0 0 presentation allowed
0 1 presentation restricted
1 0 spare
1 1 spare
bits H-C: spare
3.48 Remote operations (national use)
The format of the remote operations parameter field is shown in Figure 46. The format
and coding of the elements in the components are described in this subclause.
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
ext. |
spare |
Protocol profile |
Component(s) |
| NOTE – The component may be repeated any
number of times within the remote operations parameter. In case of multiple service
requests, the receiving entity shall treat the repetition of Invoke components identical
to the case where multiple Remote Operations parameters are received in a single message. |
Figure 46/Q.763 – Remote operations parameter field
The following codes are used in the Remote Operations parameter field:
a) Extension indicator (ext.): as Subclause 3.25 a).
b) Protocol profile field
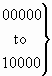 |
spare |
| 1 0 0 0 1 |
remote operations protocol |
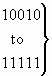 |
spare |
c) Components
This item provides the format and encoding of Component(s). The description is
divided in two sub-items.
Sub-item i) uses the description method of other Q.700-Series Recommendations. The
content is based on the encoding rules provided in Recommendation X.209 and is
consistent with that Recommendation.
Sub-item ii) uses Recommendation X.209 formal description language (ASN.1).
The general component structure and encoding rules are described in Annex B/Q.763.
i) Specification of components in table form
1) Component type
The Components are based on the Remote Operations Service Element (ROSE) of
Recommendation X.229. The four component types defined for the Remote Operation parameter
are as follows:
– Invoke;
– Return Result;
– Return Error;
– Reject.
2) Component type tag
Each Component is a sequence of information elements. The Component types have the
structure indicated in Tables 6 to 9.
The information element for the various components shown in Tables 6 to 9 are all
mandatory except the Linked ID and the parameters.
The Parameter Tag shall be any valid ASN.1 tag, depending on the type of the parameter
supplied. It can indicate either a primitive or a constructor element and refer to any of
the defined tag classes.
When the parameter element is a collection of several information elements, the
associated data type shall be derived from the Sequence, SequenceOf, Set or SetOf types.
Subclause 3.48 c) i) 6) and Table 14 define the Sequence and Set tags.
Table 6/Q.763 – Invoke component |
Invoke component |
Mandatory indication |
Component Type Tag
Component Length (Note 1) |
Mandatory |
Invoke ID Tag
Invoke ID length
Invoke ID |
Mandatory |
Linked ID Tag
Linked ID length
Linked ID |
Optional |
Operation Code Tag
Operation Code length
Operation Code |
Mandatory |
| Parameters (Notes 2 and 3) |
Optional |
| NOTE 1 – The component length is coded to
indicate the number of octets contained in the component (excluding the component type tag
and the component length octets). NOTE 2 – The coding is supplementary service
specific and the subject of other Recommendations.
NOTE 3 – It is a parameter within ROSE, but in the ISUP it is a subfield within a
field. |
Table 7/Q.763 – Return Result Component
Return Result Component |
Mandatory indication |
Component Type Tag
Component length (Note 1) |
Mandatory |
Invoke ID Tag
Invoke ID length
Invoke ID |
Mandatory |
Sequence Tag
Sequence length (Note 2) |
Optionala) |
Operation Code Tag
Operation Code length
Operation Code (Note 3) |
Optionala) (Note
4) |
| Parameters (Note 5) |
Optionala) |
| a) Omitted when no information
elements are included the parameters. NOTE 1 – The component length is coded to
indicate the number of octets contained in the component (excluding the component type tag
and the component length octets).
NOTE 2 – The sequence length is coded to indicate the number of octets contained
in the sequence (excluding the sequence type tag and the sequence length octets).
NOTE 3 – The coding is supplementary service specific and the subject of other
Recommendations.
NOTE 4 – If a result is included, then the operation value is mandatory and is the
first element in the sequence.
NOTE 5 – It is a parameter within ROSE, but in the ISUP it is a subfield within a
field. |
Table 8/Q.763 – Return Error Component
Return Error Component |
Mandatory indication |
Component Type Tag
Component length (Note 1) |
Mandatory |
Invoke ID Tag
Invoke ID length
Invoke ID |
Mandatory |
Error Code Tag
Error Code length
Error Code |
Optional |
| Parameters (Notes 2 and 3) |
Optional |
| NOTE 1 – The component length is coded to
indicate the number of octets contained in the component (excluding the component type tag
and the component length octets). NOTE 2 – The coding is supplementary service
specific and the subject of other Recommendations.
NOTE 3 – It is a parameter within ROSE, but in the ISUP it is a subfield within a
field. |
Table 9/Q.763 – Reject Component |
Reject Component |
Mandatory indication |
Component Type Tag
Component length (Note) |
Mandatory |
Invoke ID Taga)
Invoke ID length
Invoke ID |
Mandatory |
Problem Code Tag
Problem Code length
Problem Code |
Mandatory |
|
a) If the invoke ID is not available, Universal Null (see
Table 12) with Length = 0 should be used.
NOTE – The component length is coded to indicate the number of octets contained in
the component (excluding the component type tag and the component length octets). |
The Component Type Tag is coded context-specific, constructor as indicated in
Table 10.
Table 10/Q.763 – Component Type Tag |
Component Type Tag |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Invoke |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Return Result |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| Return Error |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| Reject |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3) Length of each Component or of their Information Elements
The length of the contents is coded to indicate the number of octets in the
contents. The length does not include the Tag nor the Length of the Contents octet.
The length of the contents uses the short, long or indefinite form. If the length is
less than 128 octets, the short form is used. In the short form, bit H is coded 0, and the
length is encoded as a binary number using bits A to G. The format of this length field is
shown in Figure 47.
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
0 |
msb Length of contents lsb |
Figure 47/Q.763 – Format of the length subfield (short form)
If the length is greater than 127 octets, then the long form of the length of the
contents is used. The long form length is from 2 to 127 octets long. Bit H of the first
octet is coded 1, and bits A to G of the first octet encode a number, one less, than the
size of the length in octets as an unsigned binary number whose MSB and LSB are bits G and
A respectively. The length itself is encoded as an unsigned binary number whose MSB and
LSB are bit H of the second octet and bit A of the last octet, respectively. This
binary number should be encoded in the fewest possible octets, with no leading octets
having the value 0.
The format of this length field is shown in Figure 48.
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
1 |
msb (Length of field size) - 1 lsb |
msb |
|
|
| |
Length of
contents |
|
| |
|
lsb |
| NOTE – The application of the indefinite
form of the length is not precluded depending on future application (see Annex B). |
Figure 48/Q.763 – Format of the length subfield (long form)
4) Component ID Tag
The term Component ID refers to the Invoke ID or the Linked ID.
The Component ID Tag is coded as shown in Table 11.
Table 11/Q.763 – Coding of Component ID Tag
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Invoke ID |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| Linked IDa) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
a) This tag differs from the Invoke ID,
which is coded as a Universal INTEGER, in order to distinguish it from the following tag
(Operation Code) which is also coded as a Universal INTEGER.
|
The length of a Component ID is 1 octet.
An Invoke Component has one or two Component IDs: an Invoke ID and if it is desired to
associate the Invoke with a previous Invoke, then the second or Linked ID is provided in
addition to the Invoke ID.
Return Result and Return Error Components have one Component ID, called an Invoke ID
which is the reflection of the Invoke ID of the Invoke Component to which they are
responding.
The Reject Component uses as its Invoke ID, the Invoke ID in the component being
rejected. If this ID is unavailable (e.g. due to mutilation of the message undetected by
lower layers), then the Invoke ID Tag is replaced with a universal Null Tag (which always
has length = 0) as shown in Table 12).
Table 12/Q.763 – Coding of Null Tag |
|
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Null Tag |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
If an Invoke containing both Invoke and Linked IDs is being rejected, only the Invoke
ID is used in the Reject Component.
5) Operation Code Tag
Each operation is assigned a value to identify it. Operations can be classified as
local or global operations.
A local operation code follows an Operation Code Tag and Operation Code Length. The
Operation Code Tag is coded as shown in Table 13.
Table 13/Q.763 – Coding of Operation Code Tag |
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Local Operation
Code Tag |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Global Operation
Code Tag |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
The Global Operation Code is coded as an Object Identifier, which is described in
Recommendation X.209.
6) Parameter Tag
The Parameter Tag shall be any valid ASN.1 Tag, depending on the type of the
parameter supplied. It can indicate either a primitive or a constructor element and refer
to any of the defined tag classes.
When the parameter element is a collection of several information elements, the
associated data types shall be derived from the Sequence, SequenceOf, Set or SetOf types.
The Sequence and Set Tags are coded as shown in Table 14.
Table 14/Q.763 – Coding of Sequence and Set Tag |
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Sequence Tag |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Set Tag |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
7) Error Code Tag
Each error is assigned a value to identify it. Errors can be classified as local or
global errors. A local error code follows the Error Code Tag and Error Code Length. The
Error Code Tag is coded as shown in Table 15.
Table 15/Q.763 – Coding of Error
Code Tag |
|
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
Local Error Code Tag |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Global Error Code Tag |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
The Global Error Code is coded as an Object Identifier, which is described in
Recommendation X.209.
8) Problem Code
The Problem Code consists of one of the four elements – General
Problem, Invoke Problem, Return Result Problem or Return Error Problem. The tags for these
elements are coded as shown in Table 16. Their values are shown in Tables 17 to 20.
Table 16/Q.763 – Coding of Problem Type Tags |
Problem type |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| General Problem |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Invoke |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Return Result |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| Return Error |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
Table 17/Q.763 – Coding of General Problem
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Unrecognized Componenta) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Mistyped Componenta) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Badly Structured Componenta) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| a) Components are equivalent to
ROSE Application Protocol Data Units (APDU). |
Table 18/Q.763 – Coding of Invoke
Problem |
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Duplicate Invoke ID |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Unrecognized Operation |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Mistyped parametera) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| Resource Limitation |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| Initiating Releaseb) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| Unrecognized Linked ID |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| Linked Response Unexpected |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| Unexpected Linked Operationc) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| a) Invoke parameter is equivalent
to ROSE Invoke argument.
b) ROSE uses "Initiator releasing" as only
the initiator of the underlying association may release it. In ISUP, either entity may
release the association.
c) ROSE refers to a linked operation as a child operation. |
Table 19/Q.763 – Coding of Return Result Problem
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Unrecognized Invoke ID |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Return Result Unexpected |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Mistyped Parameter |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Table 20/Q.763 – Coding of Return Error Problem
| |
H |
G |
F |
E |
D |
C |
B |
A |
| Unrecognized Invoke ID |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Return Error Unexpected |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| Unrecognized Error |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| Unexpected Error |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| Mistyped Parameter |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
ii) Specification of components in ASN.1
The tables take precedence over the ASN.1 coding.
ISUPRemoteOperations {CCITT Recommendation q763 moduleA(0)}
DEFINITIONS ::=
BEGIN
EXPORTS OPERATION, ERROR
Component ::= CHOICE { invoke [1] IMPLICIT Invoke,
returnResult [2] IMPLICIT ReturnResult,
returnError [3] IMPLICIT ReturnError,
reject [4] IMPLICIT Reject }
-- The Components are sequences of data elements.
Invoke ::= SEQUENCE { invokeID, InvokeID Type,
linkedID [0] IMPLICIT InvokeID Type OPTIONAL,
operationCode OPERATION,
parameter ANY DEFINED BY operationCode OPTIONAL }
-- ANY is filled by the single ASN.1 data
-- type following the key word PARAMETER in
-- the type definition of a particular
-- operation.
ReturnResult ::= SEQUENCE { invokeID InvokeID Type,
SEQUENCE {operationCode OPERATION,
parameters ANY DEFINED BY operationCode}OPTIONAL}
-- ANY is filled by the single ASN.1 data
-- type following the key word PARAMETER in
-- the type definition of a particular
-- operation.
ReturnResult ::= SEQUENCE { invokeID InvokeID Type,
SEQUENCE {operationCode OPERATION,
parameters ANY DEFINED BY operationCode}OPTIONAL}
-- ANY is filled by the single ASN.1 data
-- type following the key word RESULT in
-- the type definition of a particular
-- operation.
ReturnError ::= SEQUENCE { invokeID InvokeID Type
errorCode ERROR,
parameter ANY DEFINED BY errorCode
OPTIONAL }
-- ANY is filled by the single ASN.1 data
-- type following the key word PARAMETER in
-- the type definition of a particular
-- error.
Reject ::= SEQUENCE { invokeID CHOICE {InvokeID Type, NULL },
problem CHOICE {
generalProblem [0] IMPLICIT GeneralProblem,
invokeProblem [1] IMPLICIT InvokeProblem,
returnResultProblem [2] IMPLICIT ReturnResultProblem,
returnErrorProblem [3] IMPLICIT ReturnErrorProblem }}
InvokeIDType ::= INTEGER (-128 ... 127).
-- OPERATIONS
-- Operations are specified with the OPERATION MACRO. When an operation is specified,
the
-- valid parameter set, results and errors for that operation are indicated.
Default values and
-- optional parameters are permitted.
OPERATION MACRO
BEGIN ::=
TYPE NOTATION ::= Parameter Result Errors LinkedOperations
VALUE NOTATION ::= value (VALUE CHOICE {
localValue INTEGER,
globalValue OBJECT IDENTIFIER })
Parameter ::= "PARAMETER" NamedType | empty
Result ::= "RESULT" ResultType | empty
Errors ::= "ERRORS" "{"ErrorNames"}" | empty
LinkedOperations ::= "LINKED" {LinkedOperationNames"}" | empty
ResultType ::= NamedTyped | empty
Error Names ::= ErrorList | empty
Error List ::= Error | ErrorList", "Error
Error ::= value (ERROR)
-- shall reference an error value
|type
-- shall reference an error type if no error value is specified
LinkedOperationNames ::= OperationList | empty
OperationList ::= Operation | OperationList", "Operation
Operation ::= value (OPERATION)
-- shall reference an Operation Value
|type
-- shall reference an Operation type if no Operation value is specified
NamedType ::= identifiertype | type
END -- end of Operation Macro
-- ERRORS
-- Errors are specified with the ERROR MACRO. When an error is specified, the valid
parameters
-- for that error are indicated. Default values and optional parameters are permitted.
ERROR MACRO ::=
BEGIN
TYPE NOTATION ::= Parameter
VALUE NOTATION ::= value (VALUE CHOICE {
localValue INTEGER,
globalValue OBJECT IDENTIFIER} )
Parameter ::= "PARAMETER"NamedType | empty
NamedType ::= identifier type | type
END -- end of Error Macro
-- PROBLEMS
GeneralProblem ::= INTEGER { unrecognizedComponent (0)
mistypedComponent (1)
badlyStructuredComponent (2) }
InvokeProblem ::= INTEGER { duplicateInvokeID (0)
unrecognizedOperation (1)
mistypedParameter (2)
resourceLimitation (3)
initiatingRelease (4)
unrecognizedLinkedID (5)
linkedResponseUnexpected (6)
unexpectedLinkedOperation (7) }
ReturnResultProblem ::= INTEGER { unrecognizedInvokeID (0)
returnResultUnexpected (1)
mistypedParameter (2) }
ReturnErrorProblem ::= INTEGER { unrecognizedInvokeID (0)
returnErrorUnexpected (1)
unrecognizedError (2)
unexpectedError (3)
mistypedParameter (4) }
END -- end of ISUPRemoteOperation Module.
3.49 Service activation
The format of the service activation parameter field is shown in Figure 49.
| |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
Feature code 1 |
2 |
Feature code 2 |
3 |
Feature code 3 |
: |
: |
n |
Feature code n |
Figure 49/Q.763 – Service activation parameter field
The following feature codes are used in the service activation parameter field:
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
spare |
| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 |
call transfer |
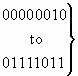 |
reserved for international use |
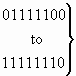 |
reserved for national use |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
reserved for extension |
Bottom Half of Document