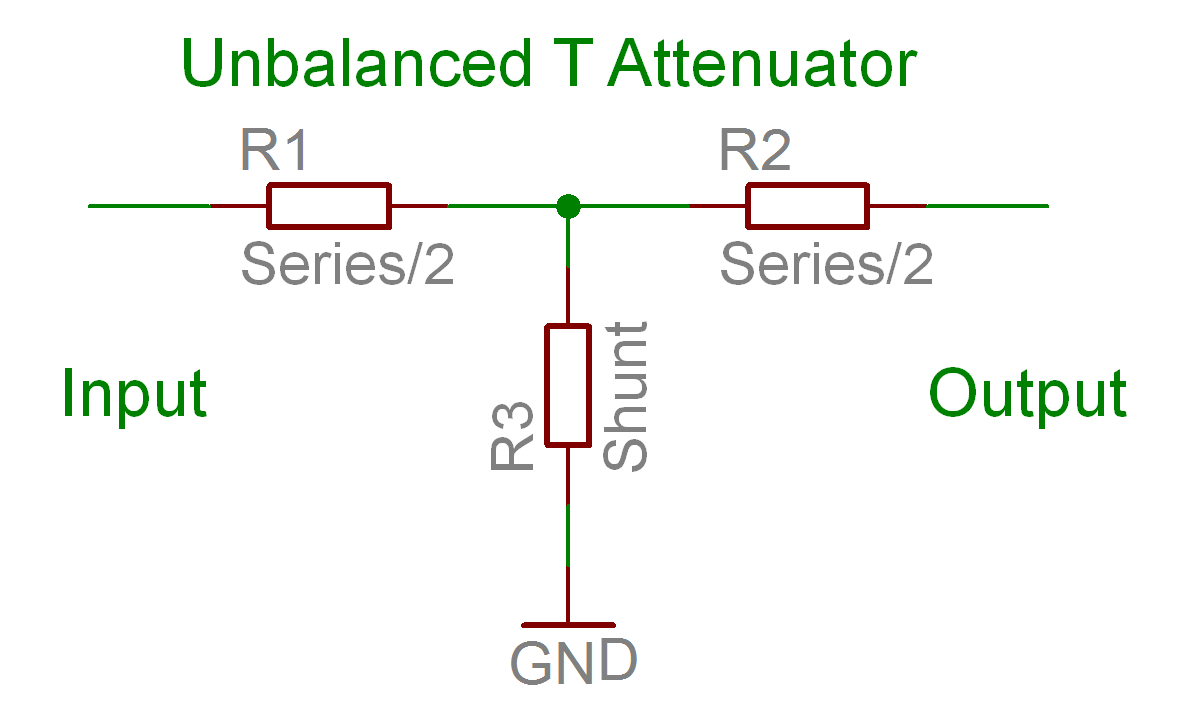

Calculates the resistor values, attenuation, minimum attenuation, impedance, reflection coefficient, VSWR and return loss of a resistive matching T attenuator.
|
|
|
The required input and output impedance are used to calculate the minimum attenuation possible for correct impedance matching with a formula from RF Design Guide, Systems, Circuits and Equations by Peter Vizmuller Published by Artech House ISBN 0-89006-754-6
![[Minimum loss possible to achieve matching formula]](matching-pi-attenuator-formula1.gif)
Where Zin is the characteristic input system impedance
Zout is the characteristic output system impedance
Peter Vizmuller also gives formulas for calculating the resistor values directly. This calculator uses formulas that I have derived and first finds the output voltage with a source EMF of 2 Volts and therefore an input PD of 1 Volt.
![[Voltage out formula]](matching-pi-attenuator-formula2.gif)
The individual ideal resistor values can now be found.
![]()
![]()
![]()
After selecting preferred values, simple series and parallel resistor calculations are used to find the attenuator input impedance, input voltage and output voltage. The source EMF is again assumed to be 2 Volts.
![[Input impedance formula]](matching-t-attenuator-formula6.gif)
![[Input Voltage formula]](matching-pi-attenuator-formula7.gif)
![[output voltage formula]](matching-t-attenuator-formula8.gif)
The remaining formulas for Attenuation, Voltage Reflection Coefficient and VSWR are available at:-
http://www.kathrein-scala.com/tech_bulletins/EngRef.pdf
Note: With the Mismatch Losses box ticked the calculator will return an attenuation calculated from the source power in relation to the attenuator output power which is suitable for calculations at RF and Microwave frequencies, particularly if the attenuator is located away from the source at the end of a transmission line. Without the Mismatch Losses box ticked the calculator will return an attenuation calculated from the actual input power to the attenuator in relation to the output power which is more suitable for calculations at audio frequencies. The difference in attenuation with the two methods is only noticeable when there is a significant mismatch.