
Orbital elements in NASA format
Les données orbitales au format NASA
Last update
2010-11-02
 ForewordThe orbital data or Keplerian elements of a satellite consist of the whole set of the parameters of his motion at a given time. Applying Kepler laws, it is possible, starting from there, to calculate the position of the satellite at any other time. By this means pass predictions can be made and the tracking achieved. The suitable software takes care of the calculus. The Keplerian elements are acquired by NORAD and transmitted to NASA wich take care of their circulation. They are available on most BBS and at AMSAT. They are presented as two lines of data as here after. The satellite is subject to external forces: solar wind, braking by hight atmosphere, path corrective firings, etc... which change its Keplerian elements. So they have to be updated on a regular basis. This is particularly necessary for manned satellites which are subjected to path corrections very often, necessitated by hight atmosphere braking.
For amateur traffic, updating on a monthly basis may be enough.
|
 Avant proposLes données orbitales ou éléments kepleriens d'un satellite sont constitués de l'ensemble des paramètres de son mouvement à un instant donné. Par l'application des lois de Kepler on peut à partir de là calculer la position du satellite à tout autre instant. C'est ainsi que l'on peut faire les prédictions de passage et assurer son suivi. Le logiciel adéquat se charge des calculs. Les éléments kepleriens sont recueillis par le NORAD et transmis à la NASA qui en assure la diffusion. Ils sont disponibles sur la plupart des BBS ainsi qu'auprès de l'AMSAT et se présentent sous la forme de deux lignes de données, comme ci-dessous. Le satellite est soumis à des forces extérieures: vent solaire, freinage par la haute athmosphère, corrections de trajectoire, etc... qui modifient ses éléments kepleriens. C'est pourquoi ceux-ci sont mis à jour régulièrement. C'est particulièrement nécessaire pour les satellites habités, lesquels font l'objet de corrections de trajectoire rendues nécessaires par suite du freinage par la haute athmosphère. Pour le trafic radioamateur, une mise à jour mensuelle peut s'avérer suffisante. |
| Two lines NASA format / Format NASA 2 lignes |
|---|
1 AAAAAU OO O O BBBBB.BBBBBBBB .CCCCCCCC OOOOO-O OOOOO-O O DDDZ 2 AAAAA EEE.EEEE FFF.FFFF GGGGGGG HHH.HHHH III.IIII JJ.JJJJJJJJKKKKKZ KEY: A-catalognum B-epochtime C-decay D-elsetnum E-inclination F-RAAN G-eccentricity H-argperigee I-mnanom J-mnmotion K-orbitnum Z-checksum |
| Example / Exemple |
|---|
Epoch time Decay rate
RS-10/11 <------------> <------->
|||||||||||||| |||||||||
1 18129U 87054A 96297.87861232 .00000076 00000-0 66627-4 0 2981
|||||
2 18129 082.9237 053.4068 0011766 150.5910 209.5908 13.72370878467828
||||| |||||||| |||||||| ||||||| |||||||| |||||||| ||||||||||||||||
<---> <------> <------> <-----> <------> <------> <---------><--->
Catalog Inclinat R.A.A.N. Eccentr Argument Mean Mean Epoch
number perigee anomaly motion rev.
|
| Glossary / Lexique | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch time | T0 | Date of the last update of orbital elements, in the example above, 96 = year, 297 = 297th day, .87861232 = fraction of a day | Date du relevé des éléments orbitaux, selon l'exemple, 96 = année, 297 = 297ème jour, .87861232 = fraction de jour |
| Decay rate | N1 | First derivative of the mean motion against time, about 10^-4 for low orbit satellites, 10^-7 for hight orbit satellites, example N1 = - 0,00000076, the duration of one revolution is reduced of 0,00000076 orbite/day per day | Dérivée première du mouvement moyen par rapport au temps, environ 10^-4 pour satellites en orbite basse, 10^-7 pour satellites en orbite haute, ex. N1 = - 0,00000076, la durée de révo lution diminue de 0,00000076 orbite/jour par jour |
| Inclination | I0 | Inclination of the orbit in degres, example I0 = 82,9237 | Inclinaison de l'orbite en degrés, exemple I0 = 82,9237 |
| R.A.A.N. | O0 | Right Ascension of Ascending Node,in degres, relatively to the vernal equinox point, in the example above O0 = 53,4068 | Ascension droite du noeud ascendant en degrés, comptée relativement a l'équinoxe vernal, dans l'exemple O0 = 53,4068 |
| Eccentricity | E0 | Excentricity of the orbital ellipse, in the example above E0 = 0,0011766 | Excentricité de l'ellipse orbitale, dans l'exemple ci-dessus E0 = 0,0011766 |
| Arg of perigee | W0 | Argument of perigee in degres, counted relatively to the ascendant node, example W0 = 150,5910 | Argument du perigée en degrés, compté relativement au noeud ascendant, exemple W0 = 150,5910 |
| Mean anomaly | M0 | Expressed in degres from 0 to 360, it is the position onto the orbit at the time T0 counted relatively to perigee, exemple M 0= 209,5908 (The phase defines the position of the satellite on its orbit at a given time, relatively to perigee, on a scale from 0 to 256) | Anomalie moyenne en degrés de 0 a 360, c'est la position sur l'orbite au temps T0 comptée relativement au périgée, exemple M0 = 209,5908. (La phase définit la position du satellite sur son orbite a un instant donné, relativement au périgée, sur une échelle de 0 à 256) |
| Mean motion | N0 | Example N0 = 13,72370878 orbits covered in 24 h, the period is equal to 24 / N0 heures | Mouvement moyen, exemple N0 = 13,72370878 orbites par 24 h, la période est de 24 / N0 hours |
| Epoch rev | K0 | Number of orbits covered since launching, exemple K0 = 46782 | Numéro de l'orbite depuis le lancement, example K0 = 46782 |
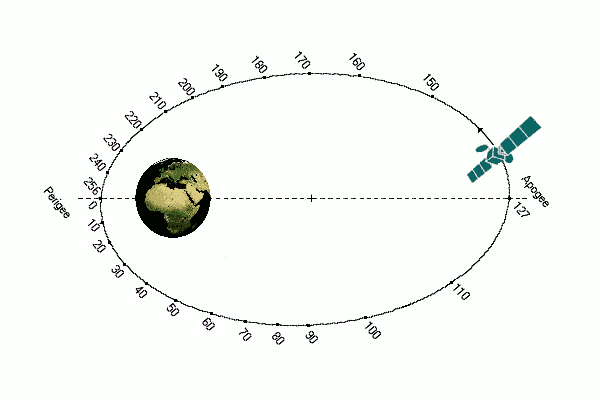
The phase defines the position of the satellite on its orbit at a given time, relatively to perigee, on a scale from 0 to 256
La phase définit la position du satellite sur son orbite a un instant donné, relativement au périgée, sur une échelle de 0 à 256
|
English bibliography
Bibliographie en français
Software
Updating orbital elements
Mise à jour des données orbitales |
|
File: orbital.html - Robert L.E. Billon, 2000-04-12 - Last update: 2010-11-02 |