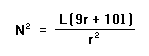
RADIO
CALCULATIONS
by Harry Lythall
Here are a few calculators for electronic/radio circuits. They are crude, but they work.
Note that the inductance unit is nano-Henries (nH) (1uH = 1000nH). Capacitance unit is pico-Farads (pf) and resistance unit is ohms. Decimals are not allowed in the input fields, if you enter a value of 1.9925 then the assumed input value will be 1.
Just add them together!
Formula: Effective Resistance = (R1 x R2) / (R1 + R2)
Formula: Reactance = 1 / (2 * Pi * F * C)
Formula: Reactance = 2 * Pi * F * L
Formula: Frequency = 1 / (2 * Pi * Sqrt(LC))
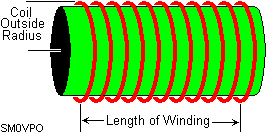
| Formula: | 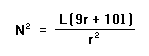 |
 |
| Formula: |  |
 |
Calculates the effective temperature rise coefficient of a measured heatsink. Area is EXPOSED surface area of heatsink in square centimeters.
| Formula: | Degrees Centigrade per Watt = 50 / Sqrt(Area sq-cm ) |
Calculates heatsink surface area needed for a given heatsink temperature coefficient.
| Formula: | Area Required (sq-cm) = Sq (50/C-watt) |

| Formulas: |
The Input/Output powers may be in any electrical unit you prefer, eg: Meggawatts, Picowatts, Joules, Hamster-treadmill revolutions per hour etc.
Negative values of resistance occur when impossible values of input and output impedance and attenuation are entered. For example, it is not possible to drive a 50-ohm line from a 600-ohm line and have a voltage attenuation factor of less than 6.78

| Formulas: | 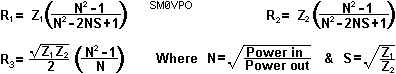 |
The Input/Output powers may be in any electrical unit you prefer, eg: Meggawatts, Picowatts, Joules, Hamster-treadmill revolutions per hour, etc.
Again, negative values indicate an impossible attenuation situation.
Ham radio Data Center - free schematics | Free HAM Directory | About me | Acronyms | CW | Data Sheets | Docs | Download | E-mail | HOME | Ham projects | Hobby circuits | Photo galery | PIC | QTH photos |
Sign in my guestbook | View my guestbook ]
© 2001 - YO5OFH, Csaba Gajdos