 |
The WB3GCK Downspout Antenna Craig LaBarge, WB3GCK |
 |
The WB3GCK Downspout Antenna Craig LaBarge, WB3GCK |
After years of trying to come up with a good way to get on the HF bands from my little townhouse (without attracting a lot of attention from my neighbors), I started experimenting with using my aluminum rain gutter and downspout for an antenna. The results have been surprisingly good. In fact, it has turned out to be the ultimate low-profile antenna!
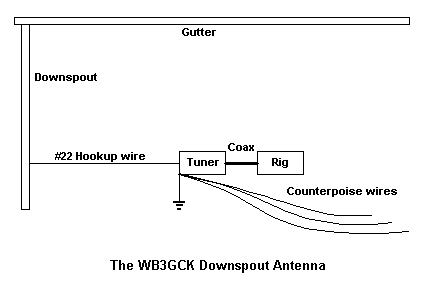
I use my downspout like a random wire antenna, using a commercial transmatch. A piece of #22 stranded hookup wire runs from the transmatch to the downspout and is attached with a sheet metal screw. The downspout has a vertical run of approximately 16 feet, connecting the horizontal rain gutter which is about 16 feet long across the front of the house. Including the feed wire into the shack, the total length is in the neighborhood of 42 feet; over a quarter wavelength for 40 meters and almost a half-wave for 30 meters. The house is made of brick, so the entire system is isolated from ground.
With the downspout behaving essentially like an end-fed wire, it really helps to work this type of antenna against a good ground. Fortunately, my basement operating position is only a few feet away from where the water supply pipe enters the house. I used a piece of 1/2-inch copper pipe as a ground bus between my operating position and the incoming water pipe. A tinned copper braid strap and a couple of ordinary automotive hose clamps were used to connect the bus to the water pipe. A short braid strap connects the ground stud on the transmatch to the copper ground bus.
For good measure, I attached counterpoise wires to the ground stud of the transmatch; one each for 40, 30, 20, and 15 meters. The counterpoise wires are made from garden variety stranded hookup wire cut to a quarter-wavelength. I just run these wires around the shack, hiding them under the rug. Operation on the 80 meter band has been successful using just the ground bus.
How well does it work? During the first few months of operation, I worked 44 states; all with 5 watts or less. I've also worked a handful of DX stations (though I'm more of a casual rag chewer than a DX-chaser). The length of the "antenna" is somewhat short for 80 meters, but performance on that band has been a big surprise. Signal reports on 30 and 40 meters, my primary bands, have been consistently good. In fact, the downspout has now become my main antenna.
Some words of caution are in order, however, if you plan to use your
rainspout as an antenna:
So, if you find your HF antenna options are limited by either space or legal restrictions, take a look at the outside of your house. There just might be a free multi-band antenna hanging out there!