manner as vacuum-tubes. Shown in the drawings below, is a comparison
between a triode vacuum-tube and a PNP transistor; where the transistor
the tube cathode, and the transistor collector is comparable to the tube plate.
|
To Bottom of Page |
Page 26 |
Return to Table of Contents |
HOME |
|
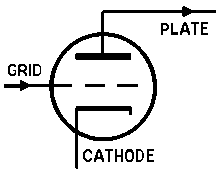
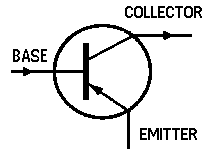
Transistors can be made to amplify, detect, or to oscillate in much the same
manner as vacuum-tubes. Shown in the drawings below, is a comparison between a triode vacuum-tube and a PNP transistor; where the transistor |
||||

|

|
|||
|
Triode Vacuum Tube |
PNP Transistor |
|||
|
base is comparable to the tube grid, the transistor emitter is comparable to the tube cathode, and the transistor collector is comparable to the tube plate. |
||||
| Transistor Formulas | Transistor Symbols | |||||
| Input resistance, |
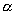
|
= | Current gain common base | |||
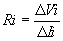
|
Ae (Av) | = | Voltage gain | |||
| Current Gain, | Ai | = | Current gain | |||
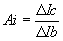 (with Vc constant)
(with Vc constant)
|
Ap | = | Power gain | |||
| Voltage Gain, | B | = | Current gain common emitter | |||
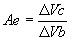 (with Ic constant)
(with Ic constant)
|
Ib | = | Base current | |||
| Ic | = | Collector current | ||||
| Output Resistance, | Ie | = | Emitter current | |||
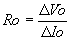
|
Ii | = | Input current | |||
| Pi | = | Input power | ||||
| Power Gain, | Po | = | Output power | |||
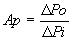
|
Ri | = | Input resistance | |||
| Ro | = | Output resistance | ||||
| The current gain of the common base | Vb | = | Base voltage | |||
| configuration is alpha, where | ||||||
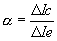 (with Vc constant)
(with Vc constant)
|
Vc | = | Collector voltage | |||
| Vi | = | Input voltage | ||||
|
The current gain of
the common emitter is beta, where |
A direct realtionship exists between the alpha and beta of a transistor. |
|||||
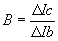 (with Vc constant)
(with Vc constant)
|
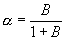
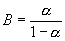
|
|||||
| Courtesy Howard W. Sam's Photofact Publication: "ABC's of Transistors." | ||||||
|
Return to top |
PAGE 26 |
Return to Table of Contents |
HOME |