Electric flux density
Magnetic Flux Density
The tables below list the systems of electrical and magnetic units.
They only include units of interest in the field of Radio.
The older systems were the CGS and Gaussian systems.The Gaussian system
being based on a mix of Electrostatic units (ESU) and Electromagnetic units
(EMU).
The current standard is the International System of Units (SI) and is
sometimes referred to as rationalised MKS units.
Conversions from one system to others are given in two ways. Firstly
numerically by multiplying factors. Note that c stands for the velocity
of light in space and its value is exactly 299792458 metre/second exactly
(by definition of the metre).
The other method of conversion allows you to change formulas given in old books into the modern SI form. This will be particularly useful to you if, like me, you have books by Terman, Scroggie, etc. or the Admiralty Handbook of Wireless Telegraphy. There were lots of useful formulas in these old books, which can now be given new life.
I have tried to make the tables as complete and accurate as possible
and have checked lots of different sources. Nevertheless there may be errors
and I will be grateful for any corrections or additions. Please email me
at the address given on the home page.
| Quantity | Symbol | Unit & (Abbr.) | Dimensions | ESU | EMU |
| Mass | m | kilogram (kg) | M | 1000 | 1000 |
| Length | l | metre (m) | L | 100 | 100 |
| Time | t | second (s) | T | 1 | 1 |
| Power | P | watt (W) | ML2T-3 | 107 | 107 |
| Electric Current | I | ampere (A) | I=M½L1½T-2 | 10c | 0.1 |
| Charge | Q | coulomb (C) | TI | 10c | 0.1 |
| Electric Potential | V | volt (V) | ML2T-3I-1 | 106/c | 108 |
| Resistance | R | ohm ( |
ML2T-3I-2 | 105/c2 | 109 |
| Conductance | G | siemens (S) | M-1L-2T3I2 | 10-5c2 | 10-9 |
| Inductance | H | henry (H) | ML2T-2I-2 | 105/c2 | 109 |
| Capacitance | C | farad (F) | M-1L-2T4I2 | 10-5c2 | 10-9 |
| Electric Field Strength | E | volt/metre (V m-1) | MLT-3I-1 | 104/c | 106 |
| Electric Charge Density | coulomb/cu.m. (C m-3) | L-3TI | c/105 | 10-7 | |
| Electric displacement
Electric flux density |
D | coulomb/sq.m. (C m-2) | L-2TI | 4 |
4 |
| Magnetic Potential | ampere (A) | I | 4 |
4 |
|
| Magnetic Field Strength | H | ampere/metre (A m-1) | L-1I | 4 |
4 |
| Magnetic flux | weber (Wb) | ML2T-2I-1 | 106/c | 108 | |
| Magnetic Induction
Magnetic Flux Density |
B | tesla (T) | MT-2I-1 | 100/c | 104 |
| Magnetic susceptibility | none | none | 10-4c-2/(4 |
1/(4 |
|
| Magnetic Moment | m | ampere metre2 (A m2) | L2I | 105c | 103 |
| Magnetisation (Magnetic moment/unit volume) | M | ampere/metre (A m-1) | L-1I | 10-1c | 10-3 |
| Magnetic Polarisation | J | tesla (T) | MT-2I-1 | 102/(4 |
104/(4 |
| Magnetic Pole Strength | P | ampere metre (A m) | LI | 103c | 10 |
| Magneto Motive Force | Fm | ampere (A) | I | 4 |
4 |
| Magnetic Reluctance | S | ampere/weber(A Wb-1) | I2M-1L-2T2 | 4 |
4 |
| Permittivity of space | farad/metre (F m-1) | M-1L-3T4I2 |
|
|
|
| Permeability of space | henry/metre (H m-1) | MLT-2I-2 |
|
|
Notes:
c (the speed of light) = 299792458 metre/second exactly (by definition
of the metre)
![]() = 1/(4
= 1/(4![]() 10-7c2)
= 8.85418781762039 x 10-12 farad/metre (approx)
10-7c2)
= 8.85418781762039 x 10-12 farad/metre (approx)
![]() = 4
= 4![]() 10-7
= 1.25663706143592 x 10-6 henry/metre (approx)
10-7
= 1.25663706143592 x 10-6 henry/metre (approx)
| Quantity | Symbol | Dimensions | Dimensions | ESU | EMU |
| Mass | m | M | M | gram | gram |
| Length | l | L | L | centimetre | centimetre |
| Time | t | T | T | second | second |
| Power | P | ML2T-3 | ML2T-3 | erg/second | erg/second |
| Electric Current | I | I | M½L1½T-2 | statamp | biot |
| Charge | Q | TI | M½L1½T-1 | franklin | abcoulomb |
| Electric Potential | V | ML2T-3I-1 | M½L½T-1 | statvolt | abvolt
(lines/second) |
| Resistance | R | ML2T-3I-2 | L-1T | statohm | abohm |
| Conductance | G | M-1L-2T3I2 | LT-1 | statsiemens | absiemens |
| Inductance | L | ML2T-2I-2 | L-1T2 | stathenry | abhenry |
| Capacitance | C | M-1L-2T4I2 | L | cm | abfarad |
| Electric field strength | E | MLT-3I-1 | M½L-½T-1 | statvolt/cm | abvolt/cm |
| Electric displacement | D | L-2TI | M½L1½T-1 | statcoulomb cm-2 | abcoulomb cm-2 |
| Dielectric constant | M-1L-3T4I2 | none | none | none | |
| Magnetic pole | P | LI | M½L2½T-2 | unit pole
dyne cm-1 = 4 |
|
| Magnetic Potential | I | M½L1½T-2 | gilbert | ||
| Magnetic field strength | H | L-1I | M½L½T-2 | oersted | |
| Magnetic flux | ML2T-2I-1 | M½L½ | maxwell
= 1 line |
||
| Magnetic Induction
(Magnetic flux density) |
B | MT-2I-1 | M½L-1½ | gauss
= 1 line cm-2 |
|
| Magnetic permeability | MLT-2I-2 | L-2T2 | darcy | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility | M½L1½T-2I-1 | none | none | none | |
| Intensity of Magnetisation | M (or I)
= J |
L-1I | M½L½T-2 | pole cm-2 | |
| Magnetic Moment | m | L2I | M½L3½T-2 | pole cm | |
| Magneto Motive force | G | I | M½L1½T-2 | gilbert | |
| Magnetic Reluctance | S | L-2M-1T2I2 | LT-2 | gilbert/biot |
Notes:
In the first column of Dimensions, I is used as a basic unit.
In the second it is expressed in terms of Length, Mass and Time.
| Quantity | Symbol | Gaussian | Modified Gaussian |
| Electric Current | I | ESU franklin | EMU biot |
| Charge | Q | ESU statcoulomb | ESU statcoulomb |
| Electric Potential | V | ESU statvolt | ESU statvolt |
| Resistance | R | ESU statohm | ESU statohm |
| Inductance | L | EMU abhenry | cm |
| Capacitance | C | cm | cm |
| Electric field strength | E | ESU statvolt/cm | ESU statvolt/cm |
| Electric displacement | D | ESU statcoulomb/cm2 | ESU statcoulomb/cm2 |
| Dielectric constant | none | none | |
| Magnetic pole | P | EMU unit pole | EMU unit pole |
| Magnetic Potential | EMU gilbert | EMU gilbert | |
| Magnetic field strength | H | EMU oersted | EMU oersted |
| Magnetic flux | EMU maxwell
= 1 line |
EMU maxwell
= 1 line |
|
| Magnetic Induction
(Magnetic flux density) |
B | EMU gauss | EMU gauss |
| Magnetic permeability | EMU darcy | EMU darcy | |
| Magnetic susceptibility | none | none | |
| Intensity of Magnetisation | M | EMU pole cm-2 | EMU pole cm-2 |
| Magnetic Moment | m | EMU pole cm | EMU pole cm |
| Magneto Motive force | G | EMU gilbert | EMU gilbert |
| Magnetic Reluctance | S | EMU | EMU |
| Quantity | Gaussian | SI |
| Electric Current | I | I / |
| Electric Current in EMU | I | |
| Charge | Q | Q / |
| Electric Potential, PD, EMF | V | |
| Resistance | R | |
| Inductance | L | |
| Capacitance | C | C / ( |
| Electric field strength | E | |
| Electric displacement | D | |
| Dielectric constant | ||
| Magnetic pole | P | |
| Magnetic Potential | ||
| Magnetic field strength | H | |
| Magnetic flux | ||
| Magnetic Induction
(Magnetic flux density) |
B | |
| Magnetic permeability | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility | ||
| Intensity of Magnetisation | I | |
| Magnetic Moment | m | |
| Magneto Motive force | G | |
| Magnetic Reluctance | S |
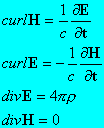
On conversion to SI units these become:
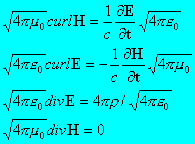
On simplifying

Then using ![]() we get:
we get:
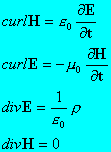
| Quantity | 1 ESU unit | 1 EMU unit |
| Current | 334 |
10 A |
| Charge | 334 |
10 C |
| Potential | 300 V | 10 nV |
| Power | 100 nW | 100 nW |
| Resistance | 90
G |
1 n |
| Conductance | 1 pS | 1 GS |
| Inductance | 90 GH | 1 nH |
| Capacitance | 1 pF | 1 GF |
| Magnetic flux | 300 Wb | 10 nWb |
| Magnetic induction | 3 MT | 100 |
| Magnetic field strength | 3 nA/metre | 80 A/metre |
| Magnetisation | 33 nA/metre | 1000 A/metre |
| Electric field strength | 30000 V/metre | 1 |
| Electric displacement | 265 nC/metre | 8000 C/metre |